Stages and treatment of covid disease (EVMS)
Updated: August 2021
Languages: German, English
Based on the available scientific evidence and current clinical experience, the SPR Collaboration recommends that physicians and authorities consider the following covid-19 treatment protocol for the prophylactic and early treatment of people at high risk or high exposure.
Numerous international studies have shown that prophylactic and early treatment can significantly reduce the risk of severe and fatal covid-19 (see scientific references below).
Note: Patients are asked to consult a doctor.
Treatment protocol
Prophylaxis
- Vitamin D3 (2000 IU per day)
- Zinc (20mg to 40mg per day)
- Quercetin (250mg per day)
- Bromhexine (24mg per day)*
- Mouthwashes and nasal spray
Early treatment
- Zinc (75mg to 100mg per day)
- Quercetin (500mg per day)
- Aspirin (325mg per day)*
- Bromhexine (48mg per day)*
- Mouthwashes and nasal spray
Prescription only
- Sulodexide (LMW heparin)*
- Fluvoxamine or cyproheptadine*
- Steroids: Prednisone or budesonide*
- High-dose vitamin D (up to 80,000 IU)*
- Monoclonal antibody treatment
- Anti-androgen treatment
- Ivermectin*
(*) Notes
- Ivermectin requires a prescription in the US and in most EU states (more).
- Bromhexine is available prescription-free in most of Europe, but not in the US.
- Cyproheptadine and steroids are only used if respiratory symptoms develop.
- Vitamin D for early treatment should be used in its fast-acting form, calcifediol.
- Counterindications and maximum dosages must be observed for all drugs.
See also
- FLCCC Covid-19 Prophylaxis and Treatment Protocols (FLCCC, May 2021)
- Early Outpatient Treatment of COVID-19 (McCullough et al., October 2020)
- Covid-19 Early Treatment Study Overview (c19early.com, April 2021)
Treatment studies
Results of trials and studies on the early treatment of covid.
Ivermectin
Ivermectin (an antiparasitic drug) has anti-viral and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Several controlled and observational studies on ivermectin found anti-viral and anti-inflammatory effects and a significant reduction in covid mortality.
- A WHO-supported meta-analysis found a reduction in covid mortality of 56%.
- However, due to a lack of large high-quality trials, the WHO, the US FDA and the European EMA do not recommend using ivermectin against covid outside of clinical trials.
- See also: The Ivermectin Debate (July 2021)
Zinc and quercetin
Zinc inhibits RNA polymerase activity of coronaviruses and thus inhibits virus replication. Quercetin (a plant polyphenol) supports the cellular absorption of zinc and has additional anti-viral properties.
- A Spanish study found that low plasma zinc levels (below 50mcg/dl) increased the risk of in-hospital death of covid patients by 130%.
- US studies found an 84% decrease in hospitalizations and a 45% decrease in mortality based on risk-stratified early treatment with zinc and HCQ.
- A US case study reported a rapid resolution of covid symptoms, such as shortness of breath, based on early outpatient treatment with high-dose zinc.
- An Italian randomized trial found a significantly reduced hospitalization rate and mortality in covid patients receiving quercetin.
Bromhexine
Bromhexine (a mucolytic cough medication) inhibits the expression of cellular TMPRSS2 protease and thus the entry of the virus into the cell, as first described in 2017.
- A randomized Iranian trial with 78 patients found a decrease in intensive care treatments of 82%, a decrease in intubations of 89%, and a decrease in deaths of 100%.
- A Chinese trial found a 50% reduction in intubations in patients receiving bromhexine.
- A Russian study found a faster recovery in hospitalized patients receiving bromhexine.
- A Russian prophylaxis study found a reduction in symptomatic covid from 20% to 0%.
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 supports and improves the immune system response to infections.
- A Spanish randomized controlled trial found a 96% reduction in the risk of requiring intensive care in patients receiving high-dose vitamin D (100,000 IU).
- Another randomized trial in Spain with 930 hospitalized patients found a reduction in ICU treatment of 80% and in mortality of 60% in patients receiving high-dose vitamin D.
- A study in a French nursing home found an 89% decrease in mortality in residents who had received high-dose vitamin D either shortly before or during covid-19 disease.
- A retrospective British study of approximately 1000 hospitalized covid patients found an 80% reduction in mortality with high-dose vitamin D.
- A large Israeli study found a strong link between vitamin D deficiency and covid-19 severity.
- For an overview of all covid-19 vitamin D studies, see here.
Aspirin and heparin
Aspirin and heparin have anti-platelet and anti-thrombotic effects.
- A meta-study including 15,000 patients found a reduction in covid mortality of 53% in patients who were receiving aspirin as early or prophylactic treatment.
- A US study found a reduction in covid mortality at 30 days from 10.5% (control group) to 4.3% (with aspirin) in veterans taking aspirin.
- A retrospective US study with 400 patients found a reduction in ICU treatments by 43% and a reduction in mortality by 47% in the group of patients treated early with aspirin.
- A Mexican randomized controlled trial found a 40% reduction in hospitalization in patients receiving sulodexide (a heparin combination).
Mouthwashes and nasal sprays
Mouthwashes and nasal sprays target the initial infection and viral replication.
- Several small studies found that mouthwashes (gargling) based on povidone-iodine and nasal sprays based on povidone-iodine or nitric oxide may prevent a coronavirus infection or reduce its duration or symptoms (more about this).
- The German Society for Hospital Hygiene (DGKH) recommends anti-viral mouthwashes and nasal sprays for prophylaxis and early treatment.
- Some observers argued that traditional nasal rinsing and gargling practices in South East Asia may have helped successfully limiting coronavirus infections in these countries.
- Israel started mass production of nasal sprays based on nitric oxide in early 2021.
Anti-androgen treatment
Anti-androgen treatment inhibits the expression of the TMPRSS2 cellular protease used by SARS-CoV-2, which is driven by androgen hormones (i.e. male sexual hormones).
- A first randomized, double-blinded and placebo-controlled trial in Brazil found that proxalutamide reduced hospitalization rates in male patients by 91%.
- Another randomized, double-blinded and placebo-controlled trial in Brazil found that proxalutamide reduced mortality in hospitalized patients (male and female) by 78%.
- Previous studies found that men receiving anti-androgens – typically used against prostate cancer or hair loss – were at a much lower risk of severe covid.
Fluvoxamine and Cyproheptadine
These drugs inhibit serotonin-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction.
- Fluvoxamine and cyproheptadine target serotonin metabolism and serotonin-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction, which according to emerging evidence appears to be a key mechanism driving severe covid and covid-related respiratory failure.
- Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and reduces platelet serotonin concentration; cyproheptadine is a direct serotonin receptor antagonist.
- The results of two preliminary US trials indicate that early treatment with fluvoxamine may reduce the risk of severe covid, hospitalization and death to near zero.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids (e.g. prednisone, budesonide) reduce covid-related systemic inflammation.
- A study by the University of Oxford, published in the Lancet, found a significant reduction in urgent care visits and hospitalizations in patients receiving budesonide (an asthma drug).
- The British PRINCIPLE trial found that budesonide accelerated recovery by 3 days and reduced hospitalizations and deaths from 10.3% to 8.5%.
- The early outpatient treatment protocol developed by McCullough et al. recommends the use of prednisone if (and only if) covid-related respiratory symptoms develop.
Monoclonal antibody therapy
Antibody therapy is intended to inhibit viral replication.
- Monoclonal antibodies have been shown to be ineffective in late treatment of covid, but very effective in early treatment. This is because severe covid is characterized by hyper-inflammation, not viral replication.
- Some monoclonal antibodies have lost their effectiveness against new virus variants.
- Convalescent plasma therapy has been shown to be ineffective in both early and late treatment of covid.
Additional notes
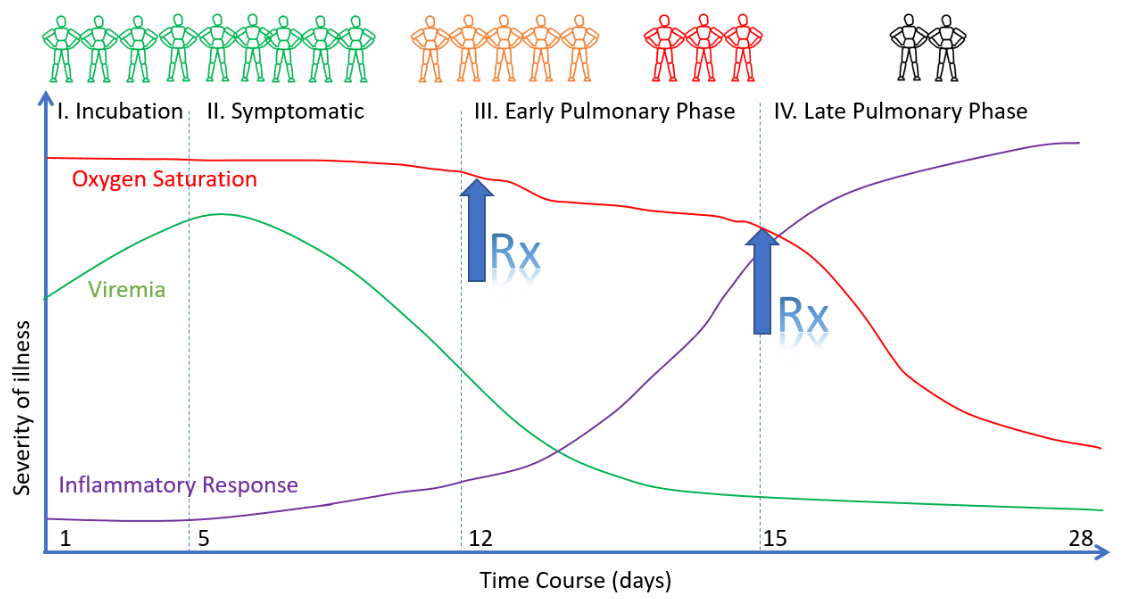
The early treatment of patients as soon as the first typical symptoms appear and even without a PCR test is essential to prevent progression of the disease. In contrast, isolating infected high-risk patients at home and without early treatment until they develop serious respiratory problems, as often happened during lockdowns, may be counterproductive.
People at high risk living in an epidemically active area should consider prophylactic treatment together with their doctor. The reason for this is the long incubation period of covid-19 (up to 14 days): when patients first notice that they contracted the disease, the viral load is already at a maximum and there are often only a few days left to react with an early treatment intervention.
Early treatment based on the above protocol is intended to avoid hospitalization. If hospitalization nevertheless becomes necessary, experienced ICU doctors recommend avoiding invasive ventilation (intubation) whenever possible and using oxygen therapy (HFNC) instead.
