
Posted on 11/19/2024 10:43:36 AM PST by Red Badger

New findings from Colorado’s rock formations provide physical evidence supporting the Snowball Earth theory, which suggests Earth was once frozen entirely, down to the equator. This study offers insights into a key phase of climate and life evolution. Credit: SciTechDaily.com Evidence from Colorado suggests glaciers once covered Earth to the equator, supporting the Snowball Earth theory. This discovery provides insight into early climate shifts and the evolution of life. Geologists have discovered compelling evidence in Colorado that hundreds of millions of years ago, enormous glaciers blanketed Earth as far as the equator, turning the planet into an icicle drifting through space.
The study, led by the University of Colorado Boulder, is a coup for proponents of a long-standing theory known as Snowball Earth. It posits that from about 720 to 635 million years ago, and for reasons that are still unclear, a runaway chain of events radically altered the planet’s climate. Temperatures plummeted, and ice sheets that may have been several miles thick crept over every inch of Earth’s surface.
“This study presents the first physical evidence that Snowball Earth reached the heart of continents at the equator,” said Liam Courtney-Davies, lead author of the new study and a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Geological Sciences at CU Boulder.
Tava Sandstone
Dark brown bands of Tava sandstone cut through other rocks. Credit: Liam Courtney-Davies
The team published its findings on November 11 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Co-authors include Rebecca Flowers, professor of geological sciences at CU Boulder, and researchers from Colorado College, the University of California, Santa Barbara, and University of California, Berkeley.
The study zeroes in on the Front Range of Colorado’s Rocky Mountains. Here, a series of rocks nicknamed the Tavakaiv, or “Tava,” sandstones hold clues to this frigid period in Earth’s past, Courtney-Davies said.
The researchers used a dating technique called laser ablation mass spectrometry, which zaps minerals with lasers to release some of the atoms inside. They showed that these rocks had been forced underground between about 690 to 660 million years ago—in all likelihood from the weight of huge glaciers pressing down above them.
Courtney-Davies added that the study will help scientists understand a critical phase in not just the planet’s geologic history but also the history of life on Earth. The first multicellular organisms may have emerged in oceans immediately after Snowball Earth thawed.
“You have the climate evolving, and you have life evolving with it. All of these things happened during Snowball Earth upheaval,” he said. “We have to better characterize this entire time period to understand how we and the planet evolved together.”
Searching for snow
The term “Snowball Earth” dates back to a paper published in 1992 by American geologist Joseph Kirschvink.
Despite decades of research, however, scientists are yet to agree whether the entire globe actually froze. Geologists, for example, have discovered the fingerprints of thick ice from this time period along ancient coastal areas, but not within the interior of continents close to the equator.
Which is where Colorado enters the picture. At the time, the region didn’t sit at the northern latitudes where it does today. Instead, Colorado rested over the equator as a landlocked part of the ancient supercontinent Laurentia.
If glaciers formed here, scientists believe, then they could have formed anywhere.
Going deep
The search for that missing piece of the puzzle brought Courtney-Davies and his colleagues to the Tava sandstones. Today, these features poke up from the ground in a few locations along Colorado’s Front Range, most notably around Pikes Peak. To the untrained eye, they might seem like ordinary-looking yellow-brown rocks running in vertical bands less than an inch to many feet wide.
But for geologists, these features have an unusual history. They likely began as sands at the surface of Colorado at some point in the past. But then forces pushed them underground—like claws digging into the Earth’s crust.
“These are classic geological features called injectites that often form below some ice sheets, including in modern-day Antarctica,” Courtney-Davies said.
He wanted to find out if the Tava sandstones were also connected to ice sheets. To do that, the researchers calculated the ages of mineral veins that sliced through those features. They collected tiny samples of the minerals, which are rich in iron oxide (essentially, rust), then hit them with a laser. In the process, the minerals released small quantities of the radioactive element uranium. Because uranium atoms decay into lead at a constant rate, the team could use them as a sort of timekeeper for the planet’s rocks.
It was a Eureka moment: The group’s findings suggest that the Tava sandstone had been pushed underground at the time of Snowball Earth. The group suspects that, at the time, thick ice sheets formed over Colorado, exposing the sands to intense pressures. Eventually, and with nowhere else to go, they pushed down into the bedrock below.
“We’re excited that we had the opportunity to unravel the story of the only Snowball Earth deposits that have so far been identified in Colorado,” Flowers said.
The researchers aren’t done yet: If such features formed in Colorado during Snowball Earth, they probably formed in other spots around North America, too, Courtney-Davies said: “We want to get the word out so that others try and find these features and help us build a more complete picture of Snowball Earth.”
Reference:
“Hematite U-Pb dating of Snowball Earth meltwater events”
by
Liam Courtney-Davies, Rebecca M. Flowers, Christine S. Siddoway, Adrian Tasistro-Hart and Francis A. Macdonald, 11 November 2024, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2410759121
Perhaps on land. Not on the oceans.
One theory is the Sun goes into a ‘cool’ period and doesn’t provide enough energy to the Earth to keep the oceans from freezing............
Trilobite farts ended that.
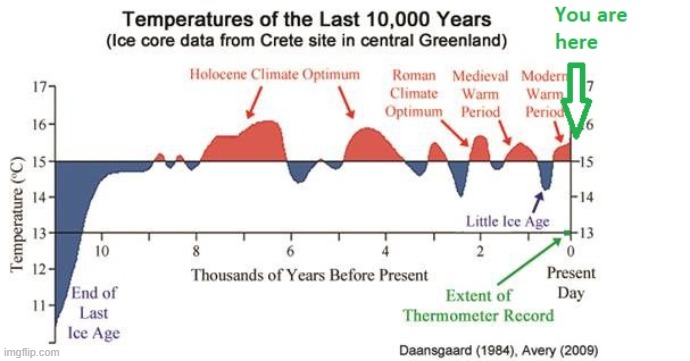
Occurring within these larger cycles that last roughly 100,000 years each:
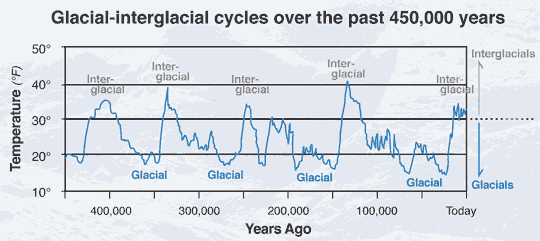
Occurring within these even larger cycles that last roughly 100,000,000 (100 million or so) years each:
It’s not dumb... The amount or water was the same, but none was in the atmosphere. It was all on the ground. That is what blew me away when I first found out that the driest desert on the planet is Antarctica with almost zero atmospheric precipitation.
I have a friend who lives in Alaska. He says that while it is cold in the winter it is not as bad as some think because it is a dry cold. All the water is frozen and laying on the ground. :)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antarctica
There’s a local beach where you can see bluffs of strata heaved up at about 45 degrees. That occurred about 14 million years ago, I believe. Atop them are a number of feet of sandstone...former ocean bottom, a hundred feet above current sea level. In the intertidal zone are some large cedar stumps, from trees that lived a few hundred years ago, that were dropped below current sea level in a big earthquake in 1700. Cascadia Subduction Zone. Hell of a ride.
And man made activity ended the glaciers, right? LOL
Thanks. I hadn’t thought about the oceans freezing (at least the upper parts) due to lack of solar radiation. So there wouldn’t necessarily be glaciers on top of the oceans - the oceans just froze up.
Thank Goodness for Globull Warming! /s
“This finding supports my theory that we are currently in an inter-glacial epoch
and that so called “climate change” and “global warming”is part of a changing and morphing continuum
which would occur regardless of human existence”
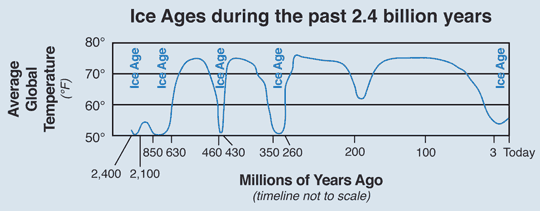
That is not a theory. That is known fact based on ice core samples. We are in an inter-glacial and the previous inter-glacial before the last ice age was even warmer with CO2 than what there is now.
This ice core sample graph at NOAA blows the climate change theory completely out of the water. No matter what we do we are headed into another ice age again. It happens on a very regular cycle. Now the only question is why?
I wonder how much this “new study” cost, and who paid for it, when it’s already been known for decades and decades.
Further, his theory about the upheavals is fascinating reading, and I believe disproving him would make a name for some scientist. None has so far.
The book is a free download at archive.org.
Red Badger’s right, as the book above shows.
Sorry. That was simpson96.
Weeeee!!! Plate tectonics and interglacial events FTW!
And given enough (geologic) time, will again! I mean, after we get through this warming phase, and the next Ice Age kicks into high gear...
Yes I remember this from grammar school
when you do not educate a couple of generations all is forgotten and they can be manipulated
Just visit one of the Mighty 5 national parks in Utah and they’ll demonstrate how the parks were formed by climate change, billions of years ago.
and then GLOBAL WARMING STARTED , OMG!!!!!!
Yup. It must have been cold. But the climate changed - it got warmer without any human assistance.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.