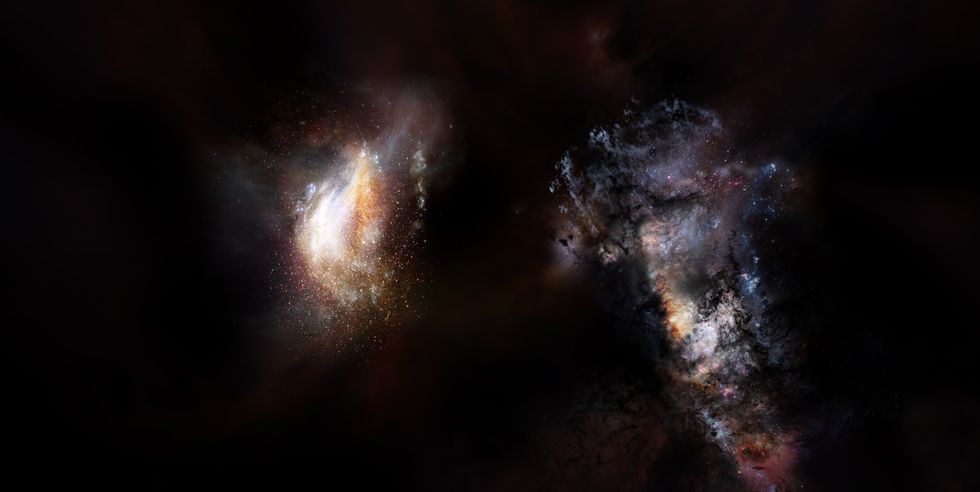 NRAO/AUI/NSF; D. Berry
NRAO/AUI/NSF; D. Berry Posted on 12/06/2017 11:31:18 AM PST by Red Badger
Less than a billion years after the Big Bang, two titans speed toward each other.
 NRAO/AUI/NSF; D. Berry
NRAO/AUI/NSF; D. Berry
=======================================================================
Just 780 million years after the universe formed in the Big Bang, two galaxies speed to confront each other in a head-on collision that will lead to a merger between the two—and one of them is towing along a clump of dark matter larger than any spotted before.
The research paper, published today in Nature, highlights a little-understood era of the universe known as the Epoch of Reionization. This is when the first galaxies came together and lit up the universe by converting hydrogen from a neutral atom to an ionized state, making the universe more transparent.
Most galaxies of the era were believed to be small, low-mass dwarf galaxies. But the results of this study—and an unrelated paper also published in Nature today that highlights a supermassive black hole from this period, the oldest ever discovered—paint a different picture of the early universe. One of the galaxies in the pair known as SPT0311-58 is only slightly less massive than the Milky Way, though the other is much smaller.
The Milky Way's mass is equal to some 480 billion suns, while SPT0311-58 has about 440 billion solar masses. The smaller galaxy in the ancient pair is about 35 billion solar masses. A halo of dark matter surrounding the two is about 100 billion solar masses.
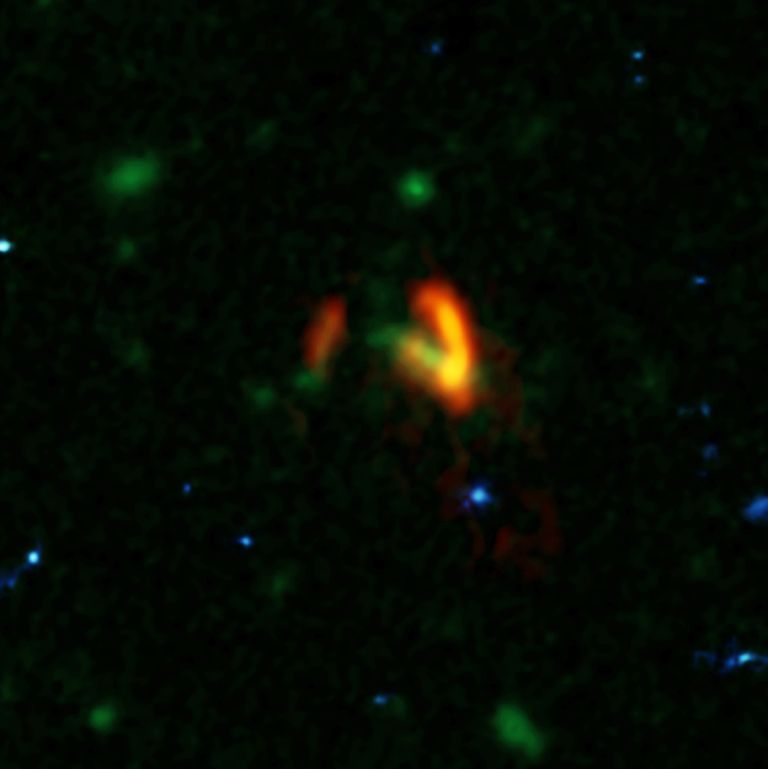
The galaxies, created via a composite image of several telescopes. ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), Marrone, et al.; B. Saxton (NRAO/AUI/NSF); NASA/ESA Hubble ==========================================================================================
Though the dark matter halo can’t be seen, its presence is inferred through gravitational interactions with the galaxies, which suggest it is enveloping both as they merge. The galaxies are messy in appearance as they haven’t had time to settle into a spiral (or other) shape due to their relative youth.
According to a NRAO press release, there are more galaxies waiting to be discovered in the same field. The pair was discovered by the South Pole Telescope, which is specifically attuned to the early universe, and follow-up observations were made with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
“Our hope is to find more objects like this, possibly even more distant ones, to better understand this population of extreme dusty galaxies and especially their relation to the bulk population of galaxies at this epoch,” said Joaquin Vieira of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in a press release.
How the first galaxies formed in the ether of the early universe is one of the biggest questions in astronomy. Studying galaxies like SPT0311-58 could help scientists understand the strange dynamics of this ancient time in the cosmos.
This doesn’t make any sense. If both galaxies date to the beginning of time, ostensibly to near the point of the “Big Bang,” they should both be moving AWAY from each other, since all matter would have scattered opposite the point of the explosion. There would have been no repelling force causing one galaxy to reverse course.
I’ve come to believe that modern cosmologists have their heads up their asses almost as much as those pushing “string theory” hand-waving.
He didn't actually 'observe' dark matter. What he did, was notice that his equations weren't balancing out the way he thought they should. So, rather than say "perhaps we need to figure out what's wrong with our current understanding of physics and cosmology, he invented something to balance things out again. I suspect we actually know less about the way things really work on both the large and small scales than we think we do.
he was playing on the Dark Side of the Moon.
That is a possibility. When cosmologists use “dark” to describe dark matter or dark energy, it doesn’t just mean we can’t see it. It also means we don’t know what it is. It could be that there is something missing in our own physics, or there is something actually out there that we can’t see. Either way, it is “dark”.
“but only because friction slows atoms down as they clumps together, rather than flying past one another.“
You sure about that?
L
I’m afraid I’m not following that. If light had traveled even faster then than its current speed that would make it even more unlikely that it would still be arriving at our position now rather than having passed by billions of years ago.
The Big Bang didn’t just occur at one point in space. It occurred everywhere, because the Big Bang is creating space as the universe expands. Furthermore, the farther you look into space, the farther back in time you’re also looking, because light from that space takes time to reach us. When you look at the Andromeda galaxy which is 2.5 million light years away, you’re looking 2.5 million years in the past. When we look 13 billion light years away, we’re seeing 13 billion years into the past, when the universe was only 1 billion years old.
“But as it’s gravitationally interactive, one would expect to see huge globules of the stuff crashing into visible bodies throughout the cosmos. Yet no such interactions are seen.”
Obviously, it must be a nonluminiferous aether so it can project a gravitational field but can’t physically interact with regular matter!
/sarc
“Modern cosmologists invented dark matter to save the Standard Model, according to which, the universe should have flown apart by now.”
I think that was actually “dark energy”, which replaced the previous fudge factor known as “the cosmological constant”. Dark matter is the other fudge factor they invented to explain why galactic motion doesn’t appear to follow the standard laws of motion and gravitation.
I ain’t no cosmologist. Though I can still see that as “everything is at the center of the universe”, as they say, that there are “epochs” which we see into gradually as our powers of magnification become greater.
When we look back 12 billion light-years, I wonder in absolute terms if what we’re seeing is even still extant.
And that it does seem all the more mysterious is part of how God designed it. And it makes me crazy as well.
what does it mean to talk about the universe expanding if the big bang occurred everywhere? How big was the universe when the big bang occurred?
If the Universe was 9 billion light years wide at the big bang and earth popped into existence 3 billion years ago at one edge Then may be we could be seeing light from 13.0 billion years ago that was generated at the far edge of the 9 billion light year wide big bang.
Q Continuum still seems more likely
I wonder how many they're up to now? Dozens? Hundreds?
The amount of patching and band-aids on the Standard Model has gotten pretty ridiculous.
But again, if the univese was once small (whatever that means), then the inflation + the speed of the galaxy through space must be near the speed of light, for earth to be in the position to receive light from 13.0 billion years ago.
Modern cosmologists have stated a great many things as fact, which are merely inferred through mathematics, not actual observation.
The Standard Model failed to explain why galaxies hang together, so the mathemagicians were forced to invent a great attractor (black holes) to patch the theory.
When they came up with Dark Matter, they lost even lay people like me.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.