Posted on 02/08/2025 1:01:46 PM PST by SunkenCiv
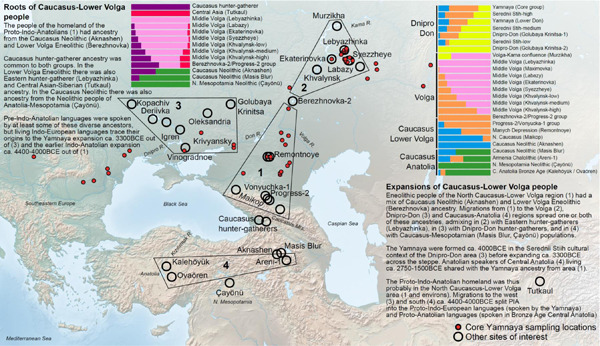
Paleoanthropologists from the University of Vienna and Harvard University have analyzed ancient DNA from 435 individuals from Eurasian archaeological sites... They've discovered a previously unknown group, called Caucasus-Lower Volga (CLV) people, and found out that this population can be connected to all Indo-European-speaking populations.
Indo-European languages, which number over 400 and include major groups such as Germanic, Romance, Slavic, Indo-Iranian, and Celtic, are spoken by nearly half the world's population today...
These migrations out of the steppes had the largest effect on European human genomes of any demographic event in the last 5,000 years and are widely regarded as the probable vector for the spread of Indo-European languages.
The only branch of Indo-European language that had not exhibited any steppe ancestry previously was Anatolian, including Hittite, probably the oldest branch to split away, uniquely preserving linguistic archaisms that were lost in all other Indo-European branches.
Previous studies had not found steppe ancestry among the Hittites because, the new paper argues, the Anatolian languages were descended from a language spoken by a group that had not been adequately described before, a Chalcolithic population...
When the genetics of this newly-recognized Caucasus-Lower Volga population are used as a source, at least five individuals in Anatolia dated before or during the Hittite era show Caucasus-Lower Volga ancestry.
The new study shows the Yamnaya population to have derived about 80% of its ancestry from the Caucasus-Lower Volga group, which also provided at least one-tenth of the ancestry of Bronze Age central Anatolians, speakers of Hittite.
(Excerpt) Read more at sci.news ...
Ooh, interesting tidbit that turned up:
Ancient DNA Reveals Asian Ancestry Introduced to East Africa in Early Modern Times
Findings clarify and complicate understanding of Swahili history
By Stephanie Dutchen
March 29, 2023
Research
6 min read
https://hms.harvard.edu/news/ancient-dna-reveals-asian-ancestry-introduced-east-africa-early-modern-times
Nice, thanks!
"Caucasus-Lower Volga"

Thanks!
Sigh....no ydna haplogroup T.
My pleasure.
How did that happen? I'd chalk it up their mixing with the Calque People.
Good luck explaining to the experts, though --
Etymology
From New Latin, from Ancient Greek χαλκός (khalkós, “copper”). Despite the appearance in English of a possible relation of chalco- to chalk, and any plausible semantic and cognate connections between limestones and ores in ancient times, the terms are not related by any known cognation. Note also the hard ch sound (/k/) in chalco- and words generated therefrom, which differs from the soft ch sound in chalk.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.