Posted on 10/18/2021 7:48:32 AM PDT by Red Badger

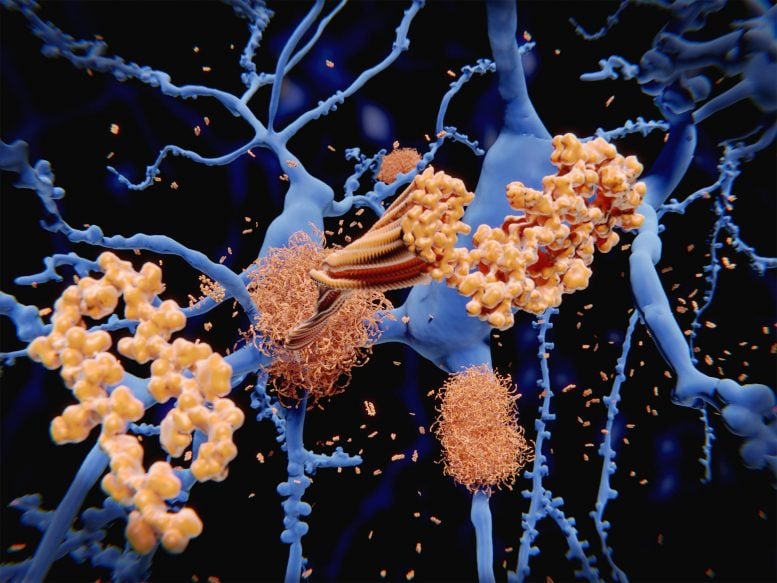
Amyloid protein (orange) forms clumps among neurons (blue). Amyloid in the brain is one of the proteins associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
================================================================================
In a major breakthrough, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have discovered how amyloid beta — the neurotoxin believed to be at the root of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) — forms in axons and related structures that connect neurons in the brain, where it causes the most damage. Their findings, published in Cell Reports, could serve as a guidepost for developing new therapies to prevent the onset of this devastating neurological disease.
Among his many contributions to research on AD, Rudolph Tanzi, PhD, vice chair of Neurology and co-director of the McCance Center for Brain Health at MGH, led a team in 1986 that discovered the first Alzheimer’s disease gene, known as APP, which provides instructions for making amyloid protein precursor (APP). When this protein is cut (or cleaved) by enzymes — first, beta secretase, followed by gamma secretase — the byproduct is amyloid beta (sometimes shortened to Abeta). Large deposits of amyloid beta are believed to cause neurological destruction that results in AD. Amyloid beta formed in the brain’s axons and nerve endings causes the worst damage in AD by impairing communication between nerve cells (or neurons) in the brain. Researchers around the world have worked intensely to find ways to block the formation of amyloid beta by preventing cleavage by beta secretase and gamma secretase. However, these approaches have been hampered by safety issues.
Despite years of research, a major mystery has remained. “We knew that Abeta is made in the axons of the brain’s nerve cells, but we didn’t know how,” says Tanzi. He and his colleagues probed the question by studying the brains of mice, as well as with a research tool known as Alzheimer’s in a dish, a three-dimensional cell culture model of the disease created in 2014 by Tanzi and a colleague, Doo Yeon Kim, PhD. Earlier, in 2013, several other MGH researchers, including neurobiologist Dora Kovacs, PhD (who is married to Tanzi), and Raja Bhattacharyya, PhD, a member of Tanzi’s lab, showed that a form of APP that has undergone a process called palmitoylation (palAPP) gives rise to amyloid beta. That study indicated that, within the neuron, palAPP is transported in a fatty vesicle (or sac) known as a lipid raft. But there are many forms of lipid rafts. “So the question was, Which lipid rafts? And which ones are most relevant to the neuronal processes making up the neural networks of the brain?” says Tanzi.
The new investigation revealed that palAPP is stabilized and prepared for cleavage by beta secretase in special lipid rafts within the neuron known as mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs). “We showed for the first time not only that the MAM is where palAPP is processed by beta secretase to make Abeta, but that this happens exclusively in axons and neuronal processes where Abeta does most of its damage,” says Bhattacharyya, lead author of the Cell Reports paper. This role for MAMs was previously unknown, though earlier research indicated that they are increased in number and activity in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
Next, the MGH team wanted to learn what happens when MAM levels and activity were intentionally altered. They showed for the first time that preventing assembly of MAMs, either with gene therapy or a drug that blocked a key protein called the sigma-1 receptor (S1R), dramatically decreased beta secretase cleavage of palAPP in axons and lowered Abeta production. Conversely, a drug that activated S1R triggered an increase in beta secretase cleavage of palAPP and increased production of amyloid beta in axons.
“Our results suggest that the sigma-1 receptor might be a viable therapeutic target for reducing Abeta production, specifically in axons,” says Tanzi. The study also lends support for a strategy already under investigation by Tanzi and his team, which is developing an experimental treatment that inhibits the palmitoylation of APP, the process that produces palAPP. It’s also known that another class of drugs that Kovacs is studying for preventing formation of amyloid beta, called ACAT inhibitors, works directly in MAMs. In the future, these and other interventions that thwart production of this most dangerous pool of axonal amyloid beta could be used in concert with early detection (through blood or imaging tests) to stop or slow the progression of AD.
Reference: “Axonal generation of amyloid-β from palmitoylated APP in mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes” by Raja Bhattacharyya, Sophia E. Black, Madhura S. Lotlikar, Rebecca H. Fenn, Mehdi Jorfi, Dora M. Kovacs and Rudolph E. Tanzi, 18 May 2021, Cell Reports. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109134
Tanzi directs the Genetics and Aging Research Unit and co-directs the Henry and Allison McCance Center for Brain Health at MGH and is the Joseph P. and Rose F. Kennedy Professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School (HMS). Bhattacharyya is also an instructor in Neurology at HMS.
This study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund.
I think short chain fatty acids are to blame for transporting it to the rain where it gets dropped off and accumulates into the plaque that causes the alzheimer., if this report goes Along with previous reports about it.
“for transporting it to the rain”
My mom always said to not stand out in the rain... she was ahead of her time...
My b key is on strike today

I should have said unsaturated fats are the transports according to previous article if I recall right, although a shirt chain fatty acids is suspected in ,alzheimers too
This should lead to therapeutics in the form of gene therapies…
—————
The flawed MRNA vaccines no doubt….the window to DNA altering and tampering has been opened. DO be aware, when God’s DNA strands are messed with, deformities, illness and really bad genetic disease ALWAYS results….I would bet a silver dollar (with “ In God We Trust” ) FEAR of Alzheimer’s will have the sheeple running to take it. Pray for Discernment.
Sorry I mean unsaturated fats, not short chain
Here is an article on it
Alzheimer’s linked to unsaturated fatty acids in the brain
I’m still getting a bigger umbrella... lol
I’d like to get rid of a pound or two..
Orange Amyloid Bad.
They figured out how one possible cause of Az is created and attaches itself to the brain. They can now focus on stopping that process. This is only one possible Az cause, so it is a breakthrough but much more...hey, did I tell you about my new dog?
Does this mean we get another mandate involving another orced drug to slow the spread of Amyloid?
Does this mean we get another mandate involving another forced drug to slow the spread of Amyloid?
Right after the forced mRNA vaccine for male-pattern baldness.
.hey, did I tell you about my new dog?
—
No. Does it bark?
Wait . . . what was I saying?
—
Was that you or your cat talking?
Yeah. Start eating keto, and take it seriously. Every day. No sugar, no carbs, no alcohol, Get your weight within guidelines. Then lose 10% more.
—
But smoking tobacco and MJ, shooting meth and heroin is fine right? I should be good then.
Dog? My coffee is cold.
Start eating keto
—
The crunchy or the smooth? Vegetarian or vegan, perhaps a little arcturian?
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.