
Posted on 06/05/2009 8:25:33 AM PDT by GodGunsGuts
“Junk” DNA: Darwinism’s Last Stand?
We are often told that the evidence for evolution is “overwhelming.” If “evolution” is defined as “change over time” or “minor changes within existing species,” this is a truism. But what if “evolution” means Charles Darwin’s theory? According to Darwin, all living things are descendants of a common ancestor that have been modified by unguided processes such as random variation and natural selection.
Despite the hype from Darwin’s followers, the evidence for his theory is underwhelming, at best. Natural selection—like artificial selection—can produce minor changes within existing species. But in the 150 years since the publication of Darwin’s Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, no one has ever observed the origin of a new species by natural selection—much less the origin of new organs and body plans. As a result, the only evidence that all living things are biologically descended from a common ancestor comes from comparisons of the similarities and differences among fossil and living species. When making such comparisons, however, Darwinists start by assuming common ancestry. Then they try to fit similarities and differences into the branching-tree pattern that would result from it, and they ignore the glaring inconsistencies that often remain.
So the evidence for anything more than minor changes within existing species is surprisingly flimsy. In most other scientific fields, a theory with so little empirical support would probably have been discarded by now. To make matters worse for Darwinism’s defenders, their theory now faces a new challenge: intelligent design (ID). According to ID, evidence from nature shows that some features of living things are explained better by an intelligent cause than by unguided natural processes.1
Junk DNA to the Rescue?
Darwin was mistaken about the origin and hereditary transmission of variations, and it wasn’t until his followers embraced Mendel’s competing theory of genetics in the 1930s that evolutionary theory began to rise to the prominence it enjoys today. According to modern neo-Darwinism, genes that are passed from generation to generation carry a program that directs embryo development; mutations occasionally alter the genetic program to produce new variations; and natural selection then sorts those mutations—the raw materials of evolution—to produce organisms better adapted to their environment.
In the 1950s, molecular biologists discovered that sequences of nucleotide subunits in an organism’s DNA encode proteins, and they equated “gene” with “protein-coding sequence.” When genetic mutations were traced to molecular accidents in the DNA, neo-Darwinian theory seemed complete. In 1970, molecular biologist Jacques Monod announced that with its “physical theory of heredity” and “the understanding of the random physical basis of mutation that molecular biology has also provided, the mechanism of Darwinism is at last securely founded. And man has to understand that he is a mere accident.”2
With design seemingly eliminated, Oxford professor Richard Dawkins wrote in 1976 that the only “purpose” of DNA is to ensure its own survival. Dawkins considered the predominant quality of successful genes to be “ruthless selfishness.” It follows that “we, and all other animals, are machines created by our genes. Like successful Chicago gangsters, our genes have survived, in some cases for millions of years, in a highly competitive world.” A body is simply “the genes’ way of preserving the genes unaltered.” Thus natural selection favors genes “which are good at building survival machines, genes which are skilled in the art of controlling embryonic development.” And genes control embryonic development by encoding proteins that build the body.3
By the 1970s, however, it was clear that most of the DNA in humans and many other animals does not code for proteins. In 1972, Susumu Ohno remarked that there is “so much ‘junk’ DNA in our genome.” 4 Dawkins was aware of this, but he argued that such junk was consistent with the logic of neo-Darwinism. “The amount of DNA in organisms,” he wrote, “is more than is strictly necessary for building them: a large fraction of the DNA is never translated into protein. From the point of view of the individual organism this seems paradoxical. If the ‘purpose’ of DNA is to supervise the building of bodies, it is surprising to find a large quantity of DNA which does no such thing. Biologists are racking their brains trying to think what useful task this apparently surplus DNA is doing. But from the point of view of the selfish genes themselves, there is no paradox. The true ‘purpose’ of DNA is to survive, no more and no less. The simplest way to explain the surplus DNA is to suppose that it is a parasite, or at best a harmless but useless passenger, hitching a ride in the survival machines created by the other DNA.”5
In 1980, Francis Crick and Leslie Orgel argued in Nature that “much DNA in higher organisms is little better than junk.” The spread of junk DNA in the course of evolution “can be compared to the spread of a not-too-harmful parasite within its host.” Since it is unlikely that such DNA has a function, “it would be folly in such cases to hunt obsessively for one.” In a companion article, W. Ford Doolittle and Carmen Sapienza similarly argued that many organisms contain “DNAs whose only ‘function’ is survival within genomes,” and that “the search for other explanations may prove, if not intellectually sterile, ultimately futile.”6
Some biologists wrote to Nature expressing their disagreement. Thomas Cavalier-Smith considered it “premature” to dismiss non-protein-coding DNA as junk, and Gabriel Dover wrote that “we should not abandon all hope of arriving at an understanding of the manner in which some sequences might affect the biology of organisms in completely novel and somewhat unconventional ways.” Orgel, Crick and Sapienza replied that “most people will agree” that higher organisms contain “parasitic” DNA or “dead” DNA. “Where people differ,” they wrote, “is in their estimates of the relative amounts. We feel that this can only be decided by experiment.”7
In 1980, the techniques for DNA sequencing were tedious and slow, but they improved rapidly. In 1990, the U.S. Department of Energy and National Institutes of Health established the Human Genome Project (HGP), with the goal of sequencing the entire human genome by 2005.8
Throughout the 1990s, however, many biologists continued to regard much of human DNA as non-functional “junk.” For example, according to the 1995 edition of Voet & Voet's Biochemistry “a possibility that must be seriously entertained is that much repetitive DNA serves no useful purpose whatever for its host. Rather, it is selfish or junk DNA, a molecular parasite.” Indeed, it may be that “a significant fraction, if not the great majority, of each eukaryotic genome is selfish DNA.”9
In the coming days I'll address the junk-DNA hypothesis in more detail.
Another thread where we might see “Science is stupid” again?
Not “science”, just some “scientists”
I was so bummed that I had to go to work without my daily dose of parody, few more minutes and it would have been a bad day indeed.

Darwin = false prophet...
Looks like this is going to become a series. Stay tuned for next installment!
Ping!
I was told by a Darwinist that the proof of evolution is that I exist.
I was a bit confused because that is a very similiar simplistic response to a belief in God for so many years.
to read later

Only Temple of Darwin fanatics think science is stupid...for falsifying their religion.
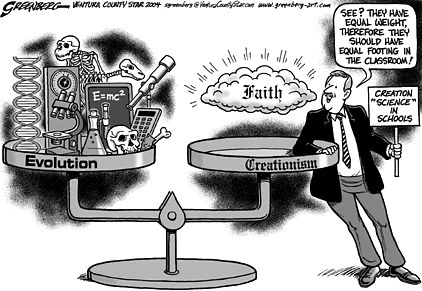

On some planet, i’m sure that makes sense, but not Earth.
I’m not taking sides in the debate, but the “science is stupid” comment is one I can’t fathom.
...who came to preach there is no god except the natural selection god.
Elucidating the form and function of the product of a strand of DNA is not as simple as simply reading the code.
The genome is documented (see human genome project) but not ALL of the genetic information is not in use at any particular stage in growth and development. While some segments may be active in embryogenesis they become dormant in the fully formed. Likewise, once differentialization occurs, the DNA within those cells will no longer function stematically and will not transcribe the unneeded segments. The function of exogenous DNA is primarily conservative, acting as a spacer, a competence check for read frame encoding as a site for restriction enzyme attachment and ligation when a frame error occurs.
Quote mining by the author from 20 or more years ago is not proof that biochemists are dimwits - it only shows how far we’ve come in our understanding of recombinant processes. Note: there is still a great deal to learn.
The Temple of Darwin Method:
We have never observed random processess plus survival evolve one organism into an entirely different kind of organsim, and yet somehow it must be true.
What I enjoy most of all about these posts, is the hysteria from those who practice at “the church of evolution, no debate possible or acceptable or other point of view allowed” religion.
The sad part about the cartoon is that it is made by someone
who obviously believes that “the western scientific method is the
final arbiter of all truth”. For a good experience talk
to someone who studies human philosophy and try and prove
that idea to them.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.