
Posted on 03/02/2021 3:17:29 PM PST by MtnClimber
Explanation: What if you could fly around Mars? NASA may have achieved that capability last month with the landing of Perseverance, a rover which included a small flight-worthy companion called Ingenuity, nicknamed Ginny. Even though Ginny is small -- a toaster-sized helicopter with four long legs and two even-longer (1.2-meter) rotors, she is the first of her kind -- there has never been anything like her before. After being deployed, possibly in April, the car-sized Perseverance ("Percy") will back away to give Ginny ample room to attempt her unprecedented first flight. In the featured artistic illustration, Ginny's long rotors are depicted giving her the lift she needs to fly into the thin Martian atmosphere and explore the area near Perseverance. Although Ingenuity herself will not fly very far, she is a prototype for all future airborne Solar-System robots that may fly far across not only Mars, but Titan.
Why would they show us an artistic rendering instead of waiting to show us the real deal?
Stop showing computer renderings or models and let’s stick to observing the real thing.
“ Surprised Mars has enough of an atmosphere for a helicopter to actually work.”
***************
Don’t forget that gravity is considerably less.
So who took that picture?
Sorry, I just now noticed the caption above the picture.......
Maxine Waters says the astronauts took the picture!
I saw your next post that you saw the text above the image, but I couldn't help it!
38% of earth gravity.
1% of earth atmospheric density.
Blade speed 5X earth helicopter speed, limited to M0.7 at the tip.


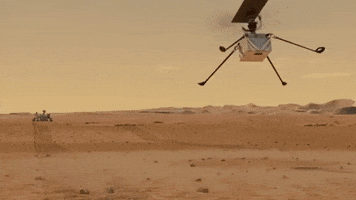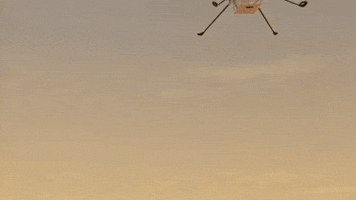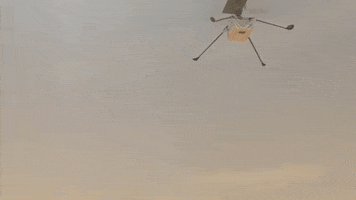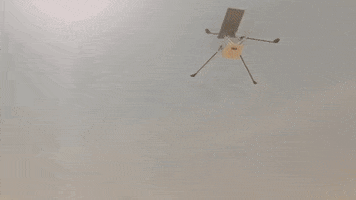
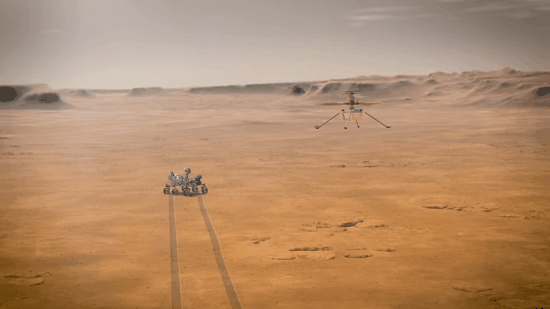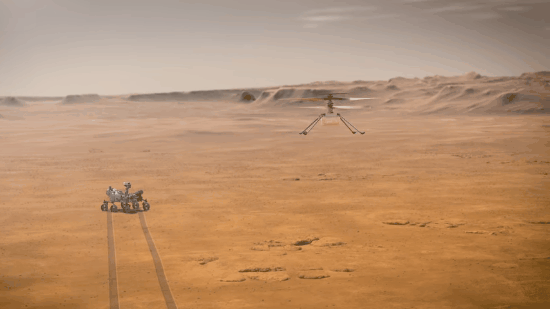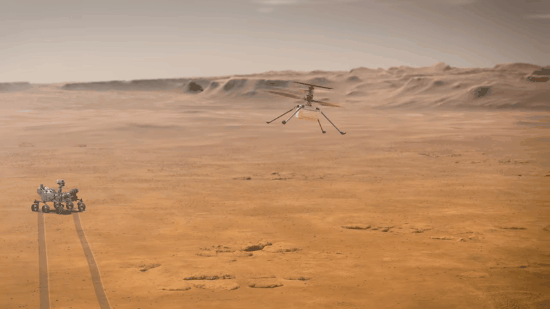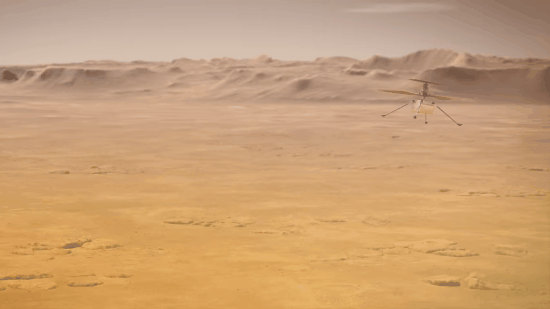


Is there really enough atmosphere for a helicopter drone to work?
Taking Flight on Another World
The Mars Helicopter, Ingenuity, is a technology demonstration to test powered flight on another world for the first time. It hitched a ride to Mars on the Perseverance rover. Once the team finds a suitable “helipad” location, the rover will release Ingenuity to perform a series of test flights over a 30-Martian-day experimental window beginning sometime in the spring.
For the first flight, the helicopter will take off a few feet from the ground, hover in the air for about 20 to 30 seconds, and land. That will be a major milestone: the very first powered flight in the extremely thin atmosphere of Mars.
After that, the team will attempt additional experimental flights of incrementally farther distance and greater altitude. After the helicopter completes its technology demonstration, Perseverance will continue its scientific mission.
https://mars.nasa.gov/technology/helicopter/
Who or how did they take this picture? Men on Mars and tall too?!?!?
Ingenuity is what is known as a technology demonstration – a project that seeks to test a new capability for the first time, with limited scope. Previous groundbreaking technology demonstrations include the Mars Pathfinder rover Sojourner and the tiny Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats that flew by Mars in 2018.
Ingenuity features four specially made carbon-fiber blades, arranged into two rotors that spin in opposite directions at around 2,400 rpm – many times faster than a passenger helicopter on Earth. It also has innovative solar cells, batteries, and other components. Ingenuity doesn’t carry science instruments and is a separate experiment from the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover.
2. Ingenuity will be the first aircraft to attempt controlled flight on another planet.
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter will make history’s first attempt at powered flight on another planet next spring. It is riding with the agency’s next mission to Mars (the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover) as it launches from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station later this summer.
What makes it hard for a helicopter to fly on Mars? For one thing, Mars’ thin atmosphere makes it difficult to achieve enough lift. Because the Mars atmosphere is 99% less dense than Earth’s, Ingenuity has to be light, with rotor blades that are much larger and spin much faster than what would be required for a helicopter of Ingenuity’s mass on Earth.
It can also be bone-chillingly cold at Jezero Crater, where Perseverance will land with Ingenuity attached to its belly in February 2021. Nights there dip down to minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 90 degrees Celsius). While Ingenuity’s team on Earth has tested the helicopter at Martian temperatures and believes it should work on Mars as intended, the cold will push the design limits of many of Ingenuity’s parts.
In addition, flight controllers at JPL won’t be able to control the helicopter with a joystick. Communication delays are an inherent part of working with spacecraft across interplanetary distances. Commands will need to be sent well in advance, with engineering data coming back from the spacecraft long after each flight takes place. In the meantime, Ingenuity will have a lot of autonomy to make its own decisions about how to fly to a waypoint and keep itself warm.
3. Ingenuity is a fitting name for a robot that is the result of extreme creativity.
High school student Vaneeza Rupani of Northport, Alabama, originally submitted the name Ingenuity for the Mars 2020 rover, before it was named Perseverance, but NASA officials recognized the submission as a terrific name for the helicopter, given how much creative thinking the team employed to get the mission off the ground.
“The ingenuity and brilliance of people working hard to overcome the challenges of interplanetary travel are what allow us all to experience the wonders of space exploration,” Rupani wrote. “Ingenuity is what allows people to accomplish amazing things.”
4. Ingenuity has already demonstrated feats of engineering.
In careful steps from 2014 to 2019, engineers at JPL demonstrated that it was possible to build an aircraft that was lightweight, able to generate enough lift in Mars’ thin atmosphere, and capable of surviving in a Mars-like environment. They tested progressively more advanced models in special space simulators at JPL. In January 2019, the actual helicopter that is riding with Perseverance to the Red Planet passed its final flight evaluation. Failing any one of these milestones would’ve grounded the experiment.
5. The Ingenuity team will count success one step at a time.
Given the firsts Ingenuity is trying to accomplish, the team has a long list of milestones they’ll need to pass before the helicopter can take off and land in the spring of 2021. The team will celebrate each time they meet one. The milestones include:
Surviving the launch from Cape Canaveral, the cruise to Mars, and landing on the Red Planet
Safely deploying to the surface from Perseverance’s belly
Autonomously keeping warm through the intensely cold Martian nights
Autonomously charging itself with its solar panel
And then Ingenuity will make its first flight attempt. If the helicopter succeeds in that first flight, the Ingenuity team will attempt up to four other test flights within a 30-Martian-day (31-Earth-day) window.
6. If Ingenuity succeeds, future Mars exploration could include an ambitious aerial dimension.
Ingenuity is intended to demonstrate technologies needed for flying in the Martian atmosphere. If successful, these technologies could enable other advanced robotic flying vehicles that might be included in future robotic and human missions to Mars. They could offer a unique viewpoint not provided by current orbiters high overhead or by rovers and landers on the ground, provide high-definition images and reconnaissance for robots or humans, and enable access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach.
“The Ingenuity team has done everything to test the helicopter on Earth, and we are looking forward to flying our experiment in the real environment at Mars,” said MiMi Aung, Ingenuity’s project manager at JPL. “We’ll be learning all along the way, and it will be the ultimate reward for our team to be able to add another dimension to the way we explore other worlds in the future.”
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/jpl/6-things-to-know-about-nasas-ingenuity-mars-helicopter

Thanks. I’m guessing the boys and girls at JPL have got this 😉...
That counter rotating two-blade design prevents the body from rotating. With one blade the body will spin the opposite direction unless it has a tail rotor to offset the “opposite and equal” spin.
And to him...

They tested helicopters on earth.
"The testing took place in the 25-foot space simulation chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California where the Martian atmosphere was reproduced."
Heh. Good one.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.