357th Fighter Group
Assigned to the 363rd Fighter Squadron, of the 357th Fighter Group, he moved up to P-39s with the squadron at Tonopah, Nevada. Unlike many other pilots, he always  liked the P-39 (which probably would have been a decent airplane if it had had a turbocharger). Here at Tonopah, he first developed the fighter pilot's detached attitude toward death, even getting angry at those he thought had died needlessly or through lack of skill. During the ruthless weeding-out process at Tonopah, the pilots worked as hard at playing as they did at flying. They frequented the bars and cathouses of Tonopah and nearby Mina, until the sheriff ran them out of the latter establishment. He and his lifelong friend, Bud Anderson, both made it through the process.
liked the P-39 (which probably would have been a decent airplane if it had had a turbocharger). Here at Tonopah, he first developed the fighter pilot's detached attitude toward death, even getting angry at those he thought had died needlessly or through lack of skill. During the ruthless weeding-out process at Tonopah, the pilots worked as hard at playing as they did at flying. They frequented the bars and cathouses of Tonopah and nearby Mina, until the sheriff ran them out of the latter establishment. He and his lifelong friend, Bud Anderson, both made it through the process.
When the squadron went to California to train for escort missions, Yeager drew temporary duty at Wright Field, Ohio, testing new props for the P-39 and also getting a chance to fly the big new P-47s. He took the opportunity to buzz his hometown, less than an hour's flying time away. As Hamlin's only fighter pilot, they knew who it was. He rejoined the squadron out in California, where he met his future wife Glennis, "pretty as a movie star and making more money than I was."
Next the squadron moved to Casper, Wyoming for more training. It was also great hunting; one time Chuck went up in his P-39 and carefully herded a dozen antelope toward a pre-arranged spot, where his armed ground confederates had a field day. They ate antelope roasts for a month. But he almost "bought the farm" in Wyoming. On October, 23, 1943, during a high speed exercise, his P-39's engine blew up, the plane burst into flames, and Yeager had to bail out. He survived, but was hospitalized with a fractured spine.
The 357th FG shipped out for Europe in winter of 1943-44, and began operations in February, 1944, the first P-51 equipped unit in the Eighth Air Force. Yeager shot down his first Messerschmitt on his seventh mission (one of the early Mustang missions over Berlin), and the next day, March 5, three FW-190s caught him and shot him down. He bailed out over occupied France, being careful to delay pulling his ripcord until he had fallen far enough to avoid getting strafed by the German fighters.
He had landed about 50 miles east of Bordeaux, injured and bleeding, but armed with a forty-five caliber pistol and determined to make his way over the Pyrenees to Spain. He hid in the woods the first night, ate a stale chocolate bar from his survival kit and huddled under this parachute. The next morning he encountered a French woodcutter.
With the Resistance
They couldn't communicate very well, but the woodcutter whispered "Boche" and gestured for Yeger to stay put. Uncertain as to the Frenchman's loyalties, but having no better choices, Yeager stayed, but trained his gun on the path when a he heard a couple people returning that night. "American, a friend is here come out." His new friends led him to a barn where he hid, while the Germans searched for him. An English-speaking woman questioned him, and satisfied that he was not a German 'plant', the local resistance people help him, starting with a local doctor who removed the shrapnel from his leg. They took him to the nearest maquis group, to hide out with them, until the snow had melted enough to permit passage over the Pyrenees. The Maquis group, about 25 men, constantly kept on the move, always being hunted by German Fieseler Storch observation planes. Yeager was an outsider with the Maquis, and sometimes relations were strained, but they accepted him when he was able to help fuse plastic explosives.
After exciting and freezing adventures, he made it over the mountains into Spain. On March 30, 1944, he sat in the American consul's office. After he languished in a Spanish hotel for six weeks, the U.S. government negotiated a deal with the Franco government - a straight swap of six evadees for an amount of Texaco gasoline. The other 357th pilots were shocked when Yeager appeared; he was the first downed pilot to have returned.
Well-considered rules forbade the return of evaded pilots to combat; if they were shot down a second time, they would be liable to reveal information about the Resistance network to the German interrogators. But Chuck Yeager would have none of it; he was determined to return to combat. The evadee rule was strict,but Yeager and a bomber pilot named Fred Glover appealed all the way to General Eisenhower, who promised to "do what he could." While the decision was pending, the Group let Yeager fly training missions. Once they were called to cover a downed pilot in the Channel, a Ju-88 appeared and Yeager couldn't restrain himself from going after it, shooting it down at the German coast. He gave the gun camera footage and the credit to another pilot, but still caught Hell.
Return to Combat
Ike decided to allow Yeager to return to combat in the summer of 1944, which he did with a vengence, now flying a P-51D nicknamed Glamorous Glen, gaudily decorated in the red-and-yellow trim of the 357th. At first, the pickings were slim, as the German fliers seemed to be laying low. He flew in a four plane division with Bud Anderson and Don Bochkay, two other double aces. On September 18, he flew in support of the Market Garden glider drops over Arnhem, but couldn't do much to stop the appalling slaughter of the C-47s. By this time, he had been promoted to Lieutenant, a commissioned officer.
in the red-and-yellow trim of the 357th. At first, the pickings were slim, as the German fliers seemed to be laying low. He flew in a four plane division with Bud Anderson and Don Bochkay, two other double aces. On September 18, he flew in support of the Market Garden glider drops over Arnhem, but couldn't do much to stop the appalling slaughter of the C-47s. By this time, he had been promoted to Lieutenant, a commissioned officer.
Yeager became an 'ace-in-a-day' on October 12, leading a bomber escort over Bremen. As he closed in on one Bf-109, the pilot broke left and collided with his wingman; both bailed out, giving Yeager credit for two victories without firing a shot. In a sharp dogfight, Yeager's vision, flying skills, and gunnery gave him three more quick kills.
The German Me-262 jets appeared in combat in late 1944, but went right after the bombers, avoiding dogfights with the Mustangs. Whenever they wanted, they could just open it up, and pull away from the P-51s with a 150 MPH speed advantage. One day Yeager caught one on its approach to an airstrip. Flying through dense flak, he downed the jet, and earned a DFC for the feat.
He flew his last "combat" mission in January, 14 1945. He and Bud Anderson cooked up a scheme to sign on for the day's missions as "spares," and then do some uninhibited flying. Anderson describes this, and other events in his life-long friendship with Yeager, in his autobiography, To Fly and Fight:
We hit the Dutch coast, took a right and flew south, 500 across France into Switzerland. Chuck was the guide. And I was the tourist. We dropped our tanks on Mount Blanc and strafed them, trying to set them afire (it seemed like a good idea at the time), then found Lake Annecy, and the lakeshore hotel where Yeager and DePaolo had met. We buzzed the hotel, fast enough and low enough to tug at the shingles, and then we zoomed over the water, right on the deck, our props throwing up mist.
We'd just shot up a mountain in a neutral country, buzzed half of Europe, and probably could have been court-martialed on any one of a half-dozen charges. It didn't matter We were aglow. It was over, we had survived, we were finished, and now we would go home together.
When we landed at Leiston, my crew chief jumped on my wing, "Group got more than 50 today. Must've been something. How many did you get?"
"None," I confessed in a small, strangled voice. I felt sick.
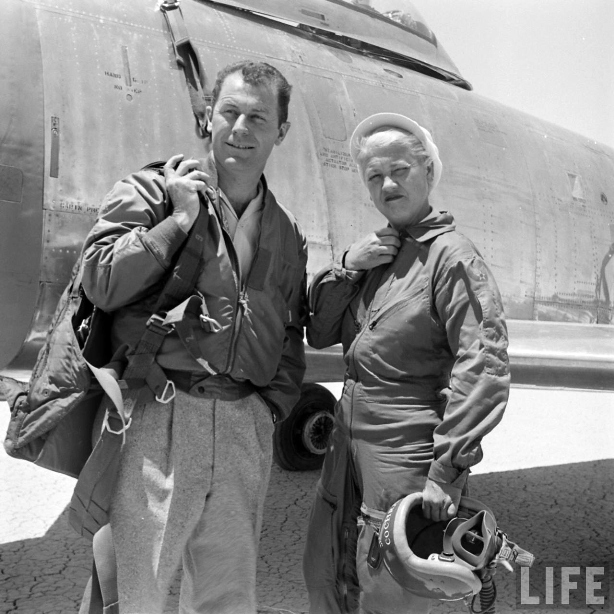
 Chuck and Glennis were married in February, and he reported to Wright Field in July, the start of his even more extraordinary career as a test pilot. He impressed his instructors so much, that despite his non-com background and his West Virginia accent, he was assigned to the XS-1 project at Muroc Field in California.
Chuck and Glennis were married in February, and he reported to Wright Field in July, the start of his even more extraordinary career as a test pilot. He impressed his instructors so much, that despite his non-com background and his West Virginia accent, he was assigned to the XS-1 project at Muroc Field in California.
Continued next week