

Posted on 03/04/2016 3:51:26 AM PST by LibWhacker
Please upgrade your Flash Plugin
The Hubble Space Telescope just calculated the distance to the most far-out galaxy ever measured, providing scientists with a look deep into the history of the universe.
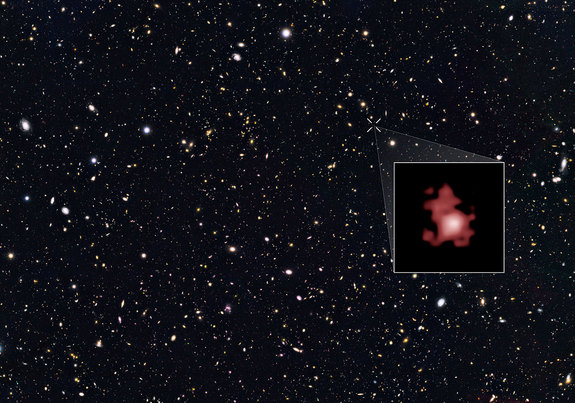
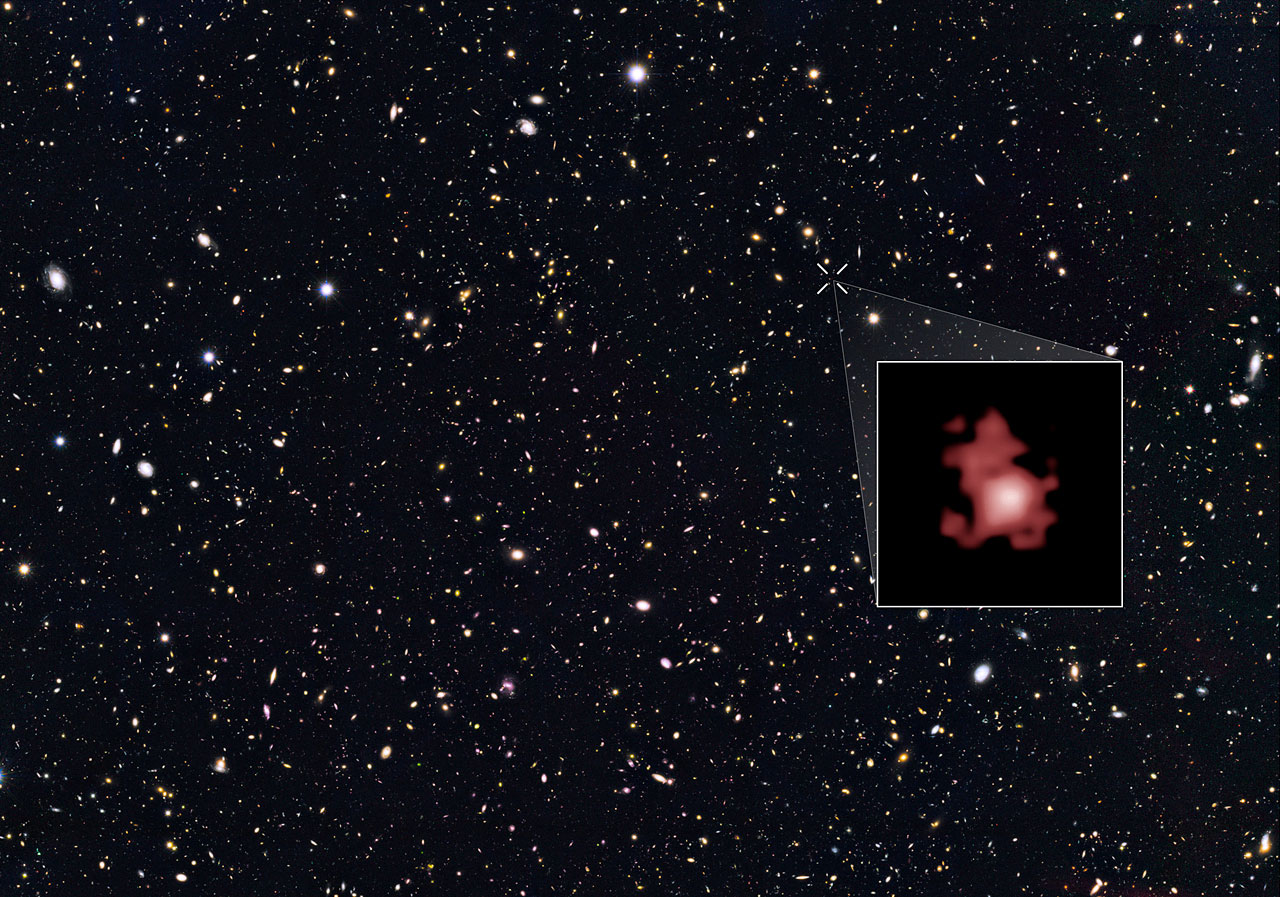
The far-away galaxy, named GN-z11, existed a mere 400 million years after the Big Bang, or about 13.3 billion years ago. Because the light from such a distant galaxy must travel huge distances to reach Earth, scientists are seeing the galaxy as it looked over 13 billion years ago. You can see the galaxy in this video from the Hubble Telescope team.
"We've taken a major step back in time, beyond what we'd ever expected to be able to do with Hubble. We managed to look back in time to measure the distance to a galaxy when the universe was only 3 percent of its current age," Pascal Oesch, an astronomer at Yale University and lead author of the research paper announcing the new measurement, said in a statement from the Hubble European Space Agency Information Centre in Germany. [Celestial Photos: Hubble Space Telescope's Latest Cosmic Views]


Measuring the distance to an extremely far-off cosmic object poses many challenges to scientists, including the fact that the universe is expanding, and has been expanding for nearly all of time. Any distance measurement must take into account exactly how much the space between objects has stretched since an object's light left and traveled to Earth.
This can get quite complicated. So instead of talking about the distance to cosmic objects in terms of miles, astronomers and astrophysicists will more often refer to when the object existed in the history of the universe.
To determine this for GN-z11, scientists measured the degree to which the light from the galaxy has been shifted by the expanding universe, known as redshift. A higher redshift indicates a more distant object. Previously, the highest redshift ever measured was from the galaxy EGSY8p7, whose redshift was 8.68. The GN-z11 galaxy's newly measured redshift is a whopping 11.1.
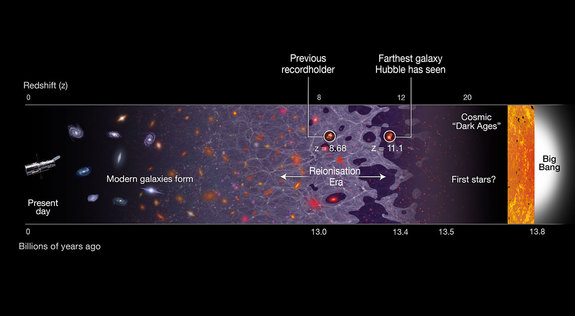
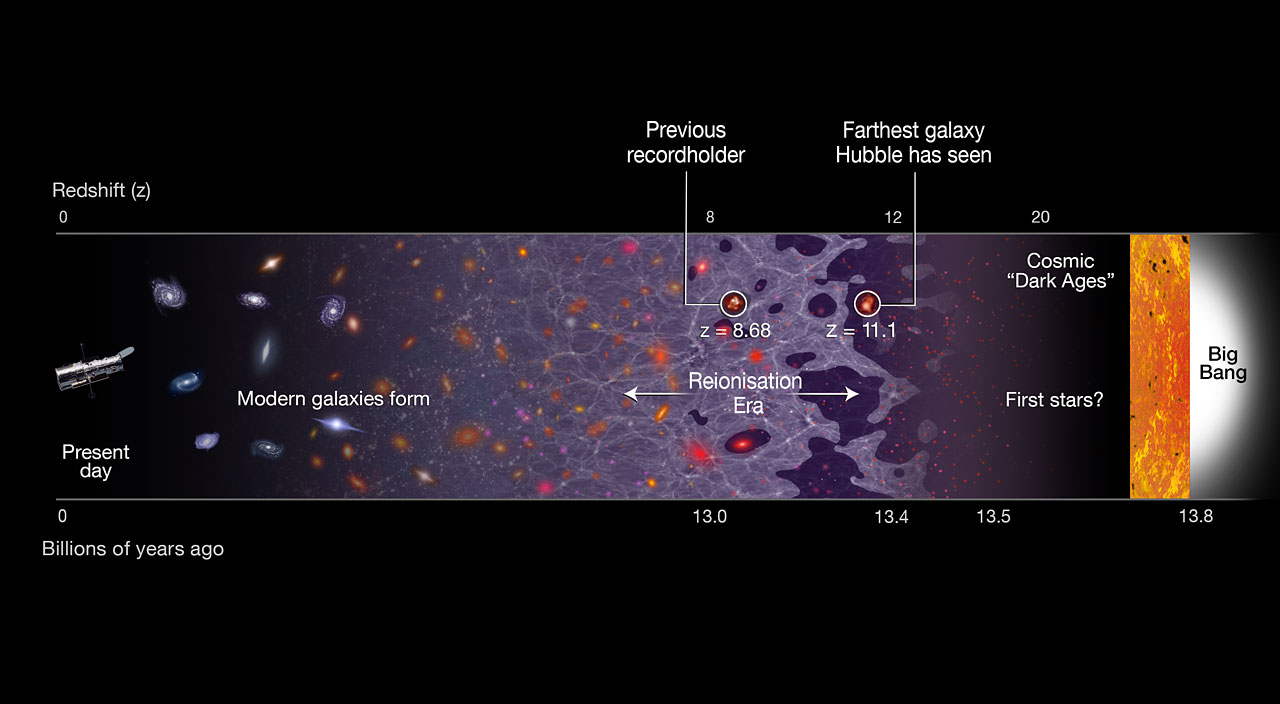
If GN-z11 existed 400 million years after the Big Bang, then it belongs to the very first population of stars and galaxies to form in the cosmos. At that time, the universe was just emerging from a period known as the Dark Ages.
"The previous record-holder was seen in the middle of the epoch when starlight from primordial galaxies was beginning to heat and lift a fog of cold, hydrogen gas," said Rychard Bouwens from the University of Leiden in the Netherlands and a co-author on the new paper. "This transitional period is known as the re-ionisation era. GN-z11 is observed 150 million years earlier, near the very beginning of this transition in the evolution of the Universe."
GN-z11 is 25 times smaller than the Milky Way galaxy and has only about 1 percent the total stellar mass of the Milky Way, observations by Hubble at the Spitzer Space Telescope have revealed, the statement said.
"It's amazing that a galaxy so massive existed only 200 million to 300 million years after the very first stars started to form," said Garth Illingworth of the University of California, Santa Cruz, a coauthor on the new research paper. "It takes really fast growth, producing stars at a huge rate, to have formed a galaxy that is a billion solar masses so soon."
GNz11 is forming stars at 20 times the current rate of the Milky Way, the statement said, which is part of why the distant galaxy is bright enough to be observed by telescopes like Hubble and Spitzer.
Marijn Franx, a member of the team from the University of Leiden, said in the statement that previous work suggested galaxies as bright as GN-z11 should not have been able to form at such an early point in the universe's history.
"The discovery of GN-z11 showed us that our knowledge about the early universe is still very restricted," said Ivo Labbe, also of the University of Leiden and a co-author on the paper. "How GN-z11 was created remains somewhat of a mystery for now. Probably we are seeing the first generations of stars forming around black holes."
Researchers said the find provides a hint at the new information that will be revealed by the James Webb Space Telescope, which is set to launch in 2018. The primary mirror on JWST is 16.4 feet (5.4 meters) wide, compared to Hubble's 7.8-foot-wide (2.4 m) mirror.
The new research paper will be published in the Astrophysical Journal.
It takes a lot of clear thinking.
His word said there was light. Good enough for me.
Clear thinking? Is that sort of like “space expands between clumps of mass”? That’s pretty impressive thinking when you consider that dust is quite evenly distributed.
That's good because NASA won't have to rename it if Hillary gets elected (now that Jim Webb says he won't vote for her).
Thanks LibWhacker.

Astronomers spot galaxy a record 13.4 billion light-years from Earth
http://www.foxnews.com/science/2016/03/04/astronomers-spot-galaxy-record-13-4-billion-light-years-from-earth.html?intcmp=trending
No, that’s sort of like math, logic and physics. Never studied them? Yeah, no kidding; there’s a reason for that.
Inflation seems a pretty good theory. And this appears to be pretty early large scale aggregation of matter.
I wonder how it eventually evolved and whether it’s still out there.
It’s actually fairly simple stuff. Einstein already said that the way to beat the speed of light was to condense space, if you take 1 unit of space and condense it to 1/4 the size you can cross THAT at less than the speed of light but get to the other side faster than light that had to go “the long way” (uncondensed). Same kind of thing happened right after the Big Bang space was condensed, travel speed ACTED faster, but really wasn’t.
It doesn’t take faith, it takes actually paying attention and not assuming you’re smarter than them. In this case it’s all about the elevator. If you can understand that you get it, if you can’t you type “riiiiiight” and act like other people are dumb.
E=mc², yet the inflationary epoch was pure energy with no matter yet congealed.
I read an article a couple of months ago about that very possibility; i.e., there may be regions of the universe still experiencing inflation. I'll see if I can dig it up for you.
Thanks, LW. Meanwhile:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eternal_inflation
I’ve been a follower - though not necessarily an advocate - of the work of Andrei Linde for some time, having attended a lecture of his at Caltech about a dozen years ago.
One really has to stretch the mind to take in some of these ideas, fascinating though they are.
I guess you’re right. Far be it for a dummy like me to dispute a brilliant astrophysicist like you.
I agree. It explains much of the currently observed universe. I'm still confused, though, about what happened BEFORE the Big Bang.
So is everyone else.
The “Big Bang”, I think, was/is a quantum event which, by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, will never be fully understood, i.e., it both did and didn’t occur.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.