To: yankeedame
ahhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh. None.
2 posted on
09/28/2008 6:53:12 AM PDT by
phatus maximus
(John 6:29...Learn it, love it, live it...)
To: yankeedame
This assumes global warming is real and still ongoing. This year the world lost a decade or two of global warming by cooling. They cannot predict the cooling cycles so they can not accurately predict the warming and ocean rise and amount of rise. I like the UN report that said 17 inches max. The ice must be hundreds of miles thick to cause hundreds of feet rise in the ocean. Lots of hot air coming out of “The Republic of Boulder”.
3 posted on
09/28/2008 6:56:19 AM PDT by
mountainlion
(concerned conservative.)
To: yankeedame
THE ACQUITTAL OF CARBON DIOXIDE by Jeffrey A. Glassman, PhD
ABSTRACT:
"Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is the product of oceanic respiration due to the well-known but under-appreciated solubility pump. Carbon dioxide rises out of warm ocean waters where it is added to the atmosphere. There it is mixed with residual and accidental CO2, and circulated, to be absorbed into the sink of the cold ocean waters. Next the thermohaline circulation carries the CO2-rich sea water deep into the ocean. A millennium later it appears at the surface in warm waters, saturated by lower pressure and higher temperature, to be exhausted back into the atmosphere. Throughout the past 420 millennia, comprising four interglacial periods, the Vostok record of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration is imprinted with, and fully characterized by, the physics of the solubility of CO2 in water, along with the lag in the deep ocean circulation.
Notwithstanding that carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, atmospheric carbon dioxide has neither caused nor amplified global temperature increases. Increased carbon dioxide has been an effect of global warming, not a cause. Technically, carbon dioxide is a lagging proxy for ocean temperatures. When global temperature, and along with it, ocean temperature rises, the physics of solubility causes atmospheric CO2 to increase.
If increases in carbon dioxide, or any other greenhouse gas, could have in turn raised global temperatures, the positive feedback would have been catastrophic. While the conditions for such a catastrophe were present in the Vostok record from natural causes, the runaway event did not occur. Carbon dioxide does not accumulate in the atmosphere."
http://www.rocketscientistsjournal.com/2006/10/co2_acquittal.html
_______________________________________________________________

The graph above represents temperature and CO2 levels over the past 400,000 years. It is the same exact data Al Gore and the rest of the man-made global warmers refer to. The blue line is temps, the red CO2 levels. The deep valleys represent 4 separate glaciation periods. Now look very carefully at the relationship between temps and CO2 levels (the present is on the right hand side of the graph) and keep in mind that Gore claims this data is the 'proof' that CO2 has warmed the earth in the past. But does the data indeed show this? Nope. In fact, rising CO2 levels all throughout this 400,000-year period actually lagged behind temperature increases ...by an average of 800 years! So it couldn't have been CO2 that got Earth out of these past glaciations. Yet Gore dishonestly and continually claims otherwise. Furthermore, the subsequent CO2 level increases due to dissolved CO2 being released from warming oceans, never did lead to additional warming, the so-called "run-away greenhouse effect" that Al Gore and his friends keep warning us about. In short, there is little if any evidence that CO2 had once led to increased warming during the past 400,000 years. -ETL
_______________________________________________________________

"The above chart shows the range of global temperature through the last 500 million years. There is no statistical correlation between the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere through the last 500 million years and the temperature record in this interval. In fact, one of the highest levels of carbon dioxide concentration occurred during a major ice age that occurred about 450 million years ago [Myr]. Carbon dioxide concentrations at that time were about 15 times higher than at present." [also see 180 million years ago, same thing happened]:
http://www.tcsdaily.com/article.aspx?id=010405M
_______________________________________________________________
So, greenhouse [effect] is all about carbon dioxide, right?
Wrong. The most important players on the greenhouse stage are water vapor and clouds. Carbon dioxide has been increased to about 0.038% of the atmosphere (possibly from about 0.028% pre-Industrial Revolution) while water in its various forms ranges from 0% to 4% of the atmosphere and its properties vary by what form it is in and even at what altitude it is found in the atmosphere.
In simple terms the bulk of Earth's greenhouse effect is due to water vapor by virtue of its abundance. Water accounts for about 90% of the Earth's greenhouse effect -- perhaps 70% is due to water vapor and about 20% due to clouds (mostly water droplets), some estimates put water as high as 95% of Earth's total tropospheric greenhouse effect (e.g., Freidenreich and Ramaswamy, 'Solar Radiation Absorption by Carbon Dioxide, Overlap with Water, and a Parameterization for General Circulation Models,' Journal of Geophysical Research 98 (1993):7255-7264).
The remaining portion comes from carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, ozone and miscellaneous other 'minor greenhouse gases.' As an example of the relative importance of water it should be noted that changes in the relative humidity on the order of 1.3-4% are equivalent to the effect of doubling CO2.
http://www.junkscience.com/Greenhouse/
_______________________________________________________________
Water Vapor Rules the Greenhouse System
Water vapor constitutes Earth's most significant greenhouse gas, accounting for about 95% of Earth's greenhouse effect (4). Interestingly, many 'facts and figures' regarding global warming completely ignore the powerful effects of water vapor in the greenhouse system, carelessly (perhaps, deliberately) overstating human impacts as much as 20-fold.
Water vapor is 99.999% of natural origin. Other atmospheric greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and miscellaneous other gases (CFC's, etc.), are also mostly of natural origin (except for the latter, which is mostly anthropogenic).
Human activities contribute slightly to greenhouse gas concentrations through farming, manufacturing, power generation, and transportation. However, these emissions are so dwarfed in comparison to emissions from natural sources we can do nothing about, that even the most costly efforts to limit human emissions would have a very small-- perhaps undetectable-- effect on global climate.
http://www.geocraft.com/WVFossils/greenhouse_data.html
4 posted on
09/28/2008 6:56:38 AM PDT by
ETL
(Smoking gun evidence on ALL the ObamaRat-commie connections at my newly revised FR Home page)
To: yankeedame
If you look at the chart below, you will see that sunspot activity (during solar maxes--the individual peaks) has been relatively high since about 1900 and almost non-existent for the period between about 1625 and 1725. This period is known as the Maunder (sunspot) Minimum or "Little Ice Age".

From BBC News [yr: 2004]:
"A new [2004] analysis shows that the Sun is more active now than it has been at anytime in the previous 1,000 years. Scientists based at the Institute for Astronomy in Zurich used ice cores from Greenland to construct a picture of our star's activity in the past. They say that over the last century the number of sunspots rose at the same time that the Earth's climate became steadily warmer."..."In particular, it has been noted that between about 1645 and 1715, few sunspots were seen on the Sun's surface. This period is called the Maunder Minimum after the English astronomer who studied it. It coincided with a spell of prolonged cold weather often referred to as the "Little Ice Age". Solar scientists strongly suspect there is a link between the two events - but the exact mechanism remains elusive."
http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/3869753.stm
It's really hard to imagine how this little ball of fire could have any impact on our climate at all.
But the main arguments being made for a solar-climate connection is not so much to do with the heat of the Sun but rather with its magnetic cycles. When the Sun is more magnetically active (typically around the peak of the 11 year sunspot cycle --we are a few yrs away at the moment), the Sun's magnetic field is better able to deflect away incoming galactic cosmic rays (highly energetic charged particles coming from outside the solar system). The GCRs are thought to help in the formation of low-level cumulus clouds -the type of clouds that BLOCK sunlight and help cool the Earth. So when the Sun's MF is acting up (not like now -the next sunspot max is expected in about 2012), less GCRs reach the Earth's atmosphere, less low level sunlight-blocking clouds form, and more sunlight gets through to warm the Earth's surface...naturally. Clouds are basically made up of tiny water droplets. When minute particles in the atmosphere become ionized by incoming GCRs they become very 'attractive' to water molecules, in a purely chemical sense of the word. The process by which the Sun's increased magnetic field would deflect incoming cosmic rays is very similar to the way magnetic fields steer electrons in a cathode ray tube or electrons and other charged particles around the ring of a subatomic particle accelerator.-ETL
____________________________________________________
There's a relatively new book out on the subject titled The Chilling Stars. It's written by one of the top scientists advancing the theory (Henrik Svensmark).

http://www.sciencedaily.com/books/t/1840468157-the_chilling_stars_the_new_theory_of_climate_change.htm
And here is the website for the place where he does his research:
2008: "The Center for Sun-Climate Research at the DNSC investigates the connection between variations in the intensity of cosmic rays and climatic changes on Earth. This field of research has been given the name 'cosmoclimatology'"..."Cosmic ray intensities – and therefore cloudiness – keep changing because the Sun's magnetic field varies in its ability to repel cosmic rays coming from the Galaxy, before they can reach the Earth." :
http://www.spacecenter.dk/research/sun-climate


100,000-Year Climate Pattern Linked To Sun's Magnetic Cycles:
ScienceDaily (Jun. 7, 2002) HANOVER, N.H.
Thanks to new calculations by a Dartmouth geochemist, scientists are now looking at the earth's climate history in a new light. Mukul Sharma, Assistant Professor of Earth Sciences at Dartmouth, examined existing sets of geophysical data and noticed something remarkable: the sun's magnetic activity is varying in 100,000-year cycles, a much longer time span than previously thought, and this solar activity, in turn, may likely cause the 100,000-year climate cycles on earth. This research helps scientists understand past climate trends and prepare for future ones.
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2002/06/020607073439.htm
From a well-referenced wikipedia.com column (see wiki link for ref 14):
"Sunspot numbers over the past 11,400 years have been reconstructed using dendrochronologically dated radiocarbon concentrations. The level of solar activity during the past 70 years is exceptional — the last period of similar magnitude occurred over 8,000 years ago. The Sun was at a similarly high level of magnetic activity for only ~10% of the past 11,400 years, and almost all of the earlier high-activity periods were shorter than the present episode.[14]"
[14] ^Solanki, Sami K.; Usoskin, Ilya G.; Kromer, Bernd; Schüssler, Manfred & Beer, Jürg (2004), “Unusual activity of the Sun during recent decades compared to the previous 11,000 years”, Nature 431: 1084–1087, doi:10.1038/nature02995, . Retrieved on 17 April 2007 , "11,000 Year Sunspot Number Reconstruction". Global Change Master Directory. Retrieved on 2005-03-11.
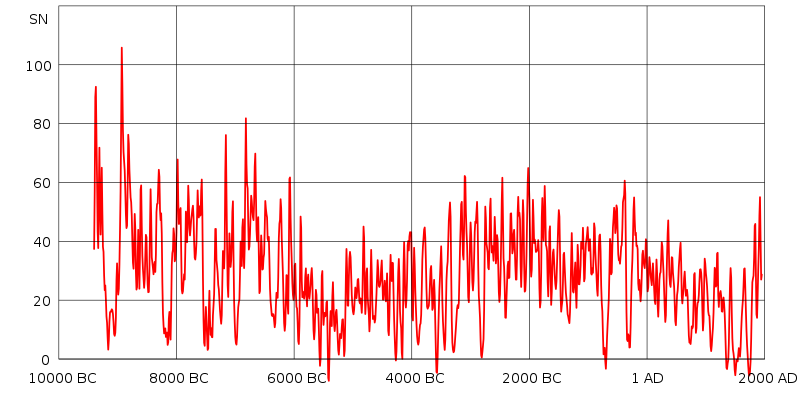
"Reconstruction of solar activity over 11,400 years. Period of equally high activity over 8,000 years ago marked.
Present period is on [the right]. Values since 1900 not shown."
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_variation
5 posted on
09/28/2008 6:57:39 AM PDT by
ETL
(Smoking gun evidence on ALL the ObamaRat-commie connections at my newly revised FR Home page)
To: yankeedame
Depends if they are over land are water?? But the Arctic cap is is getting bigger I think..
6 posted on
09/28/2008 7:03:38 AM PDT by
org.whodat
(Republicans should support the SAM Walton business model, and then drill???)
To: yankeedame
The wild rice crop in N. Minnesota failed this year. Too cold.
7 posted on
09/28/2008 7:06:37 AM PDT by
DManA
To: yankeedame
"...A Deep Thaw: How Much Will Vanishing Glaciers Raise Sea Levels...?"
Hopefully enough to cover Manhattan and Hollywood.
8 posted on
09/28/2008 7:08:01 AM PDT by
conservativeharleyguy
(Taxation is to patriotism as insubordination is to disclipline.)
To: yankeedame
“The Laurentide ice sheet that stretched as far south as New York State and Ohio some 20,000 years ago had retreated to eastern Canada, just across the water from Greenland, by roughly 11,000 years ago thanks to increased sunlight (due to the periodic wobble in Earth’s axis known as precession).”
False. Everybody knows that global warming is Man’s Fault.
9 posted on
09/28/2008 7:08:53 AM PDT by
Travis McGee
(--- www.EnemiesForeignAndDomestic.com ---)
To: yankeedame
10 posted on
09/28/2008 7:09:42 AM PDT by
Tarpon
(Barrack Obama will ban all the guns he has the votes for ...)
To: yankeedame
I was watching an old movie last night, a lot of the shots were along the cliffs on the California coastline. I was shocked at what I was seeing gelogically, which I guarantee were ancient shorlines and water levels etched in the cliff face (you see the same sorts of things here in Nevada along dried up ancient lake beds).
The point is, I don’t think what we are seeing is abnormal at all, if we are indeed seeing any global warming.
12 posted on
09/28/2008 7:17:26 AM PDT by
FastCoyote
(I am intolerant of the intolerable.)
To: yankeedame
How much water in a glass rises when the ice melts? Zero.
13 posted on
09/28/2008 7:18:17 AM PDT by
Bommer
(Who was Obama's diction coach? Bevis or Butthead? Uhhhhhh.....)
To: yankeedame
Is there anywhere where one can make a bet with these stupid Gorebots about sea-level rise? I would bet on no discernible difference within five years, i.e. less than one inch, or one and a half times the standard error of measurement - whichever is greater - for any standard technique of measurement (Gorebot's choice).
ML/NJ
16 posted on
09/28/2008 7:30:13 AM PDT by
ml/nj
To: yankeedame; enough_idiocy; rdl6989; IrishCatholic; Normandy; Delacon; ...
To: yankeedame; All
NASA article from 2004...
March 5, 2004: Global warming could plunge North America and Western Europe into a deep freeze, possibly within only a few decades.
That's the paradoxical scenario gaining credibility among many climate scientists. The thawing of sea ice covering the Arctic could disturb or even halt large currents in the Atlantic Ocean. Without the vast heat that these ocean currents deliver--comparable to the power generation of a million nuclear power plants--Europe's average temperature would likely drop 5 to 10°C (9 to 18°F), and parts of eastern North America would be chilled somewhat less. Such a dip in temperature would be similar to global average temperatures toward the end of the last ice age roughly 20,000 years ago. ..."
http://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2004/05mar_arctic.htm?list1101254
20 posted on
09/28/2008 8:12:10 AM PDT by
ETL
(Smoking gun evidence on ALL the ObamaRat-commie connections at my newly revised FR Home page)
To: yankeedame; All
The "Grim Realities" of Global COOLING"The central fact is that after three quarters of a century of extraordinarily mild conditions, the earth's climate seems to be cooling down. Meteorologists disagree about the cause and extent of the cooling trend, as well as over its specific impact on local weather conditions. But they are almost unanimous in the view that the trend will reduce agricultural productivity for the rest of the century. If the climatic change is as profound as some of the pessimists fear, the resulting famines could be catastrophic."
The Cooling World
Newsweek, April 28, 1975
There are ominous signs that the Earth's weather patterns have begun to change dramatically and that these changes may portend a drastic decline in food production– with serious political implications for just about every nation on Earth. The drop in food output could begin quite soon, perhaps only 10 years from now. The regions destined to feel its impact are the great wheat-producing lands of Canada and the U.S.S.R. in the North, along with a number of marginally self- sufficient tropical areas – parts of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Indochina and Indonesia – where the growing season is dependent upon the rains brought by the monsoon.
The evidence in support of these predictions has now begun to accumulate so massively that meteorologists are hard-pressed to keep up with it. In England, farmers have seen their growing season decline by about two weeks since 1950, with a resultant overall loss in grain production estimated at up to 100,000 tons annually. During the same time, the average temperature around the equator has risen by a fraction of a degree – a fraction that in some areas can mean drought and desolation. Last April, in the most devastating outbreak of tornadoes ever recorded, 148 twisters killed more than 300 people and caused half a billion dollars' worth of damage in 13 U.S. states.
To scientists, these seemingly disparate incidents represent the advance signs of fundamental changes in the world's weather. The central fact is that after three quarters of a century of extraordinarily mild conditions, the earth's climate seems to be cooling down. Meteorologists disagree about the cause and extent of the cooling trend, as well as over its specific impact on local weather conditions. But they are almost unanimous in the view that the trend will reduce agricultural productivity for the rest of the century. If the climatic change is as profound as some of the pessimists fear, the resulting famines could be catastrophic.
"A major climatic change would force economic and social adjustments on a worldwide scale," warns a recent report by the National Academy of Sciences, "because the global patterns of food production and population that have evolved are implicitly dependent on the climate of the present century."
A survey completed last year by Dr. Murray Mitchell of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration reveals a drop of half a degree in average ground temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere between 1945 and 1968. According to George Kukla of Columbia University, satellite photos indicated a sudden, large increase in Northern Hemisphere snow cover in the winter of 1971-72. And a study released last month by two NOAA scientists notes that the amount of sunshine reaching the ground in the continental U.S. diminished by 1.3% between 1964 and 1972.
To the layman, the relatively small changes in temperature and sunshine can be highly misleading. Reid Bryson of the University of Wisconsin points out that the Earth's average temperature during the great Ice Ages was only about seven degrees lower than during its warmest eras – and that the present decline has taken the planet about a sixth of the way toward the Ice Age average. Others regard the cooling as a reversion to the "little ice age" conditions that brought bitter winters to much of Europe and northern America between 1600 and 1900 – years when the Thames used to freeze so solidly that Londoners roasted oxen on the ice and when iceboats sailed the Hudson River almost as far south as New York City.
Just what causes the onset of major and minor ice ages remains a mystery. "Our knowledge of the mechanisms of climatic change is at least as fragmentary as our data," concedes the National Academy of Sciences report. "Not only are the basic scientific questions largely unanswered, but in many cases we do not yet know enough to pose the key questions."
Meteorologists think that they can forecast the short-term results of the return to the norm of the last century. They begin by noting the slight drop in overall temperature that produces large numbers of pressure centers in the upper atmosphere. These break up the smooth flow of westerly winds over temperate areas. The stagnant air produced in this way causes an increase in extremes of local weather such as droughts, floods, extended dry spells, long freezes, delayed monsoons and even local temperature increases – all of which have a direct impact on food supplies.
"The world's food-producing system," warns Dr. James D. McQuigg of NOAA's Center for Climatic and Environmental Assessment, "is much more sensitive to the weather variable than it was even five years ago." Furthermore, the growth of world population and creation of new national boundaries make it impossible for starving peoples to migrate from their devastated fields, as they did during past famines.
Climatologists are pessimistic that political leaders will take any positive action to compensate for the climatic change, or even to allay its effects. They concede that some of the more spectacular solutions proposed, such as melting the Arctic ice cap by covering it with black soot or diverting arctic rivers, might create problems far greater than those they solve. But the scientists see few signs that government leaders anywhere are even prepared to take the simple measures of stockpiling food or of introducing the variables of climatic uncertainty into economic projections of future food supplies. The longer the planners delay, the more difficult will they find it to cope with climatic change once the results become grim reality.
[end]
The Cooling World:
http://denisdutton.com/cooling_world.htm
Original Newsweek article with scary maps and graphs:
http://denisdutton.com/newsweek_coolingworld.pdf
21 posted on
09/28/2008 8:16:59 AM PDT by
ETL
(Smoking gun evidence on ALL the ObamaRat-commie connections at my newly revised FR Home page)
To: yankeedame
22 posted on
09/28/2008 8:21:35 AM PDT by
kabar
(.)
To: yankeedame
If melting ice raises the level of the ocean, how come when the ice melts in my single malt scotch drink the level of the liquid goes down?
23 posted on
09/28/2008 9:09:19 AM PDT by
yazoo
To: yankeedame
Answer: Sea levels may drop. As floating ice in the arctic melts and land based ice in the antarctic grows, the level of the oceans should drop because the oceans contain less water.
Glad I could help.
26 posted on
09/28/2008 1:03:27 PM PDT by
Poser
(Willing to fight for oil)
To: yankeedame
Still very very quiet on the solar front. Got Cosmic Radiation cream?
27 posted on
09/28/2008 1:52:07 PM PDT by
PA Engineer
(Liberate America from the occupation media.)
FreeRepublic.com is powered by software copyright 2000-2008 John Robinson









