
Posted on 09/24/2021 12:18:16 PM PDT by Red Badger

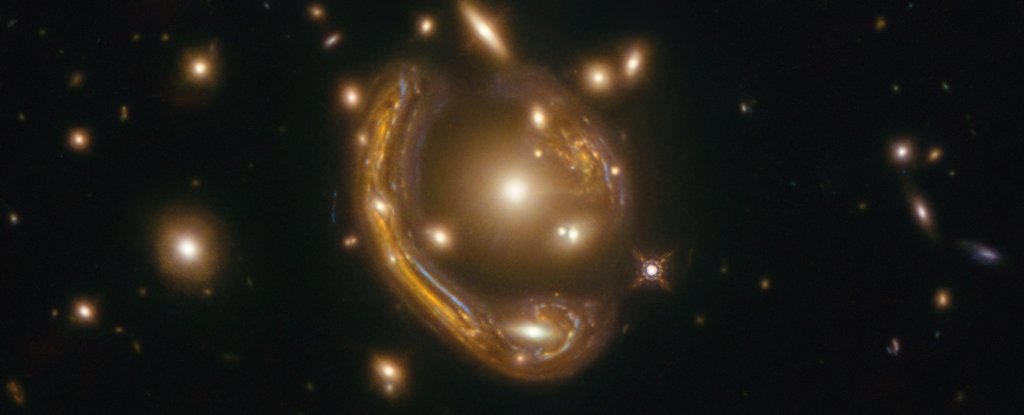
The Molten Ring. (Saurabh Jha/Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey)
One of the most spectacular Einstein rings ever seen in space is enabling us to see what's happening in a galaxy almost at the dawn of time.
The smears of light called the Molten Ring, stretched out and warped by gravitational fields, are magnifications and duplications of a galaxy whose light has traveled a whopping 9.4 billion light-years. This magnification has given us a rare insight into the stellar 'baby boom' when the Universe was still in its infancy.
The early evolution of the Universe is a difficult time to understand. It blinked into existence as we understand it roughly 13.8 billion years ago, with the first light emerging (we think) around 1 billion years later. Light traveling for that amount of time is faint, the sources of it small, and dust obscures much of it.
Even the most intrinsically luminous objects are extraordinarily hard to see across that gulf of space-time, so there are large gaps in our understanding of how the Universe assembled itself from primordial soup.
But sometimes the Universe itself offers us a helping hand. If a massive object sits between us and a more distant object, a magnification effect occurs due to the gravitational curvature of space-time around the closer object.
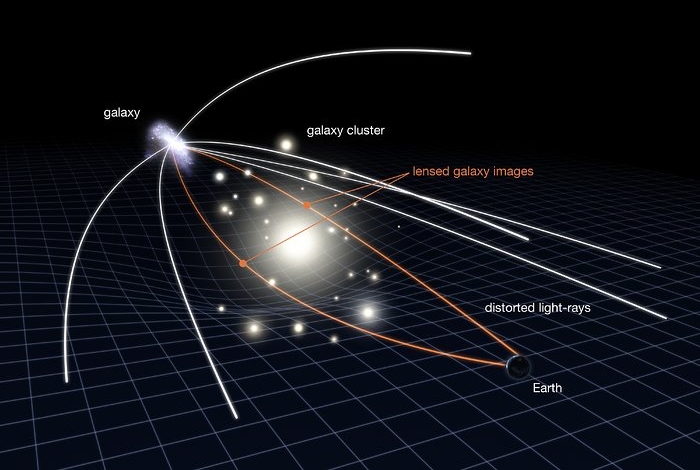
Illustration of gravitational lensing. (NASA, ESA & L. Calçada)
Any light that then travels through this space-time follows this curvature and enters our telescopes smeared and distorted – but also magnified and duplicated. These are called Einstein rings, because the effect was predicted by, you guessed it, Albert Einstein.
The phenomenon itself is called gravitational lensing, and while it has given us some absolutely amazing images, it also affords us brilliant opportunities to combine our own magnification capabilities – telescopes – with those of the Universe to see things that might otherwise be too far to make out clearly, or at all.
The Molten Ring (formally named GAL-CLUS-022058s) is just such an Einstein ring, magnified by the gravitational field around a huge cluster of galaxies in the constellation of Fornax. So powerful is this effect that not only does the distant galaxy appear in four distorted images, it's magnified by a factor of 20.
When combined with the Hubble Space Telescope, the resulting images are as detailed and sharp as observations taken with a telescope with a huge 48-meter aperture. From this, a team of researchers led by Anastasio Díaz-Sánchez of the Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena in Spain worked out that light from the galaxy has traveled 9.4 billion light-years.
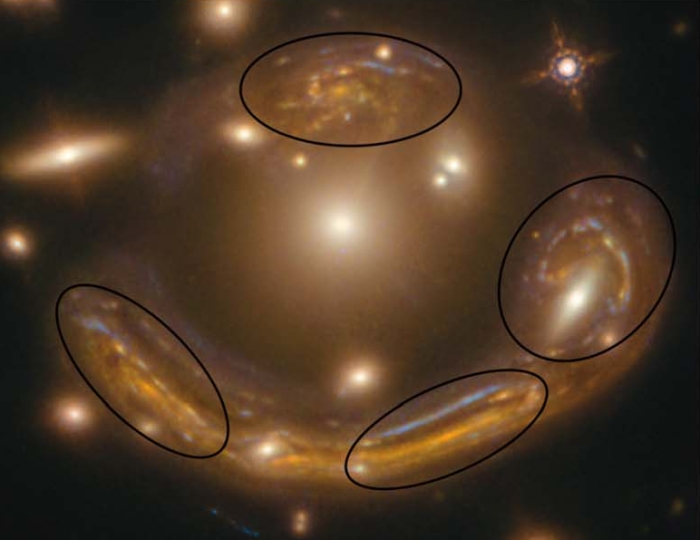
The four images of the galaxy. (Díaz-Sánchez et al., ApJ, 2021)
This means it hails from a time in which star formation was happening at a tremendous rate – a thousand times faster than star formation in the Milky Way today. Learning more about this star-forming period in the Universe's history can help us understand how today's galaxies evolved. Usually we can't see into galaxies back then very well, however; in addition to the distance, they're very dusty.
With Hubble's images, the researchers were able to model the lensing effect to rebuild the smears and duplications of the Molten Ring into the galaxy that created it.
"Such a model could only be obtained with the Hubble imaging," Díaz-Sánchez said. "In particular, Hubble helped us to identify the four duplicated images and the stellar clumps of the lensed galaxy."
This revealed that the galaxy is on what is called the main sequence of star forming galaxies – a correlation between galaxy mass and star formation rate – with new stars being born at a rate of 70 to 170 solar masses per year. The Milky Way, by contrast, has a star formation rate of just a few solar masses per year.
There's a lot we still don't know about the early Universe, and how the stars formed – but chance alignments such as the Molten Ring are helping us uncover their secrets.
The research has been published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Ping!...................
It’s Sauron...
Looks like God’s initials to me.
That long ago it probably doesn’t exist anymore, at least not in that shape.
“It blinked into existence...” amazing the nonsense people will believe.
As opposed to what?
Bookmark
Ya I'm a science guy for sure but I always find this big bang theory to be just total nonsense. It's just a way of stating the truth which is we don't have the first clue about the origins of the universe.
Wild!
I’ve always said that atheists have have more (misplaced) faith than anyone.
Surely, you don’t believe that voodoo about God creating the universe? Big Bang was responsible for it. They even know when Mr. Bang did it. Crazy, no leap of faith there.
Excerpts:
Einstein ring
An Einstein ring, also known as an Einstein–Chwolson ring or Chwolson ring (named for Orest Khvolson), is created when light from a galaxy or star passes by a massive object en route to the Earth. Due to gravitational lensing, the light is diverted, making it seem to come from different places. If source, lens, and observer are all in perfect alignment, the light appears as a ring.
[...]
The bending of light by a gravitational body was predicted by Albert Einstein in 1912, a few years before the publication of general relativity in 1916 (Renn et al. 1997). The ring effect was first mentioned in the academic literature by Orest Khvolson in a short article in 1924, in which he mentioned the “halo effect” of gravitation when the source, lens, and observer are in near-perfect alignment.[5] Einstein remarked upon this effect in 1936 in a paper prompted by a letter by a Czech engineer, R W Mandl [1], but stated
“Of course, there is no hope of observing this phenomenon directly. First, we shall scarcely ever approach closely enough to such a central line. Second, the angle β will defy the resolving power of our instruments.”
— Science vol 84 p 506 1936
[...]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Einstein_ring
I’m glad that Michelle Starr explained that Einstein rings are named for Albert Einstein. Otherwise I would have thought they were named for the Einstein Brothers who started that coffee-and-bagels chain.
How often have you said it?
Metal poor stars. Don’t you need at least two super nova explosions to create what we have here?
‘Q’ may have been born then.
The universe is (nearly) 14 billion years old, astronomers confirm. With looming discrepancies about the true age of the universe, scientists have taken a fresh look at the observable (expanding) universe and have estimated that it is 13.77 billion years old (plus or minus 40 million years).Jan 8, 2021
Astronomers reevaluate the age of the universe | Space
https://www.space.com › universe-age-14-billion-years-old
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.