Pseudoscience is a scientific-sounding argument which in fact has no scientific validity whatsoever. This type of argument is based on the fact that the average layperson knows so little about science that he or she is liable to judge a scientific argument solely on its style and presentation (eg- "does it sound scientific?", or "does it incorporate scientific-sounding terms?") for lack of any other method of judging its validity.
![]()
Suggested Tactics
This type of creationist argument is difficult for most people to defend against, unless they are fairly knowledgeable about science (that's why it's so popular with creationists- they may not know anything about science, but they're gambling that you don't either). In my case, I simply call upon my knowledge of certain basic scientific principles that I learned in university, but I can't instruct everyone to do this, since not everyone has a technical background.
Therefore, it's difficult for me to recommand tactics for laypeople to counteract this sort of argument, but we should keep in mind that creationist pseudoscience arguments are almost never generated out of the mind of the creationist himself. They all tend to come from the same widely distributed pool of creationist literature, which is one of the reasons that creationists all over the world tend to spout the same pseudoscience arguments. I can offer the following suggestions:
![]() Remember that if your opponent has no direct knowledge of the science involved, and is merely claiming truth because "I read it somewhere", this constitutes a fallacious appeal to authority. Point this out to him. One should always be able to explain the logic and science behind one's argument rather than simply making vague reference to an anonymous source.
Remember that if your opponent has no direct knowledge of the science involved, and is merely claiming truth because "I read it somewhere", this constitutes a fallacious appeal to authority. Point this out to him. One should always be able to explain the logic and science behind one's argument rather than simply making vague reference to an anonymous source.
![]() Since these arguments are actually second hand arguments, demand to see the original source for his claim. When you see the source, check the credentials of the author. If they aren't fraudulent, check up on the university where the author got his degree. Odds are that the degree is either honorary, or it comes from a cheap diploma mill (or worse yet, one of the many church-run schools set up expressly for the purpose of handing out degrees to creationists). If you don't have the resources to check up on universities, try looking up the Talk.Origins website at www.talkorigins.org, which maintains a list of discredited creationist "experts" and their bogus credentials.
Since these arguments are actually second hand arguments, demand to see the original source for his claim. When you see the source, check the credentials of the author. If they aren't fraudulent, check up on the university where the author got his degree. Odds are that the degree is either honorary, or it comes from a cheap diploma mill (or worse yet, one of the many church-run schools set up expressly for the purpose of handing out degrees to creationists). If you don't have the resources to check up on universities, try looking up the Talk.Origins website at www.talkorigins.org, which maintains a list of discredited creationist "experts" and their bogus credentials.
Examples follow:
![]()
"Occam's Razor is a scientific principle which says that when faced with two theories, we should always choose the simplest theory. Evolution theory requires billions of years of chemical reactions, environmental effects, and genetic mutations. Creation theory simply says "God did it". Creation theory is obviously simpler, therefore Occam's Razor demands that we must select Creation theory on scientific grounds."
This is perhaps the single most moronic creationist idea I've ever heard (it's also been used to "prove" the existence of God, by arguing that the concept of God is much simpler than the study of science). It's a classic example of creationist pseudoscience. They learn the term "Occam's Razor" and they learn just enough about its definition to abuse it, but they make no effort whatsoever to learn its true meaning.
"Choose the simplest theory" is an oversimplification of the concept of Occam's Razor. The term is named after the 14th century philosopher and theologian William of Occam. It might strike some as strange that a scientific principle might have come from a theologian, but good scientists do not practice appeals to authority or ad hominem attacks. If an idea makes sense, it doesn't matter who it came from, and the universal acceptance of Occam's Razor is a perfect example of that philosophy.
In any case, he argued that we should never "multiply entities unnecessarily". In other words, cut out extraneous terms from an equation. He used that principle (which is really just an argument against redundancy) to show that it was impossible to deduce God's existence through reason alone, so one would have to take it purely on faith. The irony is that a theologian realized that there was no logical basis for God's existence more than 600 years ago but modern fundamentalists still can't figure it out, and actually use his name to "prove" the exact opposite of what he himself argued!
For those who cannot appreciate the simplicity of Occam's Razor in its original form, Isaac Newton restated it thusly: "We are to admit no more causes of natural things than such as are both true and sufficient to explain their appearances." In plain English, when faced with two scientific theories which make the same predictions, choose the simpler theory. Or, as Stephen Hawking put it: "Cut out all the features of the theory which cannot be observed." (taken from A Brief History of Time).
Like all scientific principles, Occam's Razor is accepted not because William of Occam said it, but because it makes sense. You don't need to appeal to authority or take its validity on faith. If you are faced with two competing theories between which you have no other method of deciding, is it not obvious that the theory containing extra or unverifiable terms must therefore contain redundancies? The fact that the simpler theory can accomplish the same descriptive and predictive feats while utilizing fewer terms and not relying on unverifiable or unobservable phenomena is evidence of superiority.
Consider the analogy of two mechanical devices for making widgets. Both perform exactly the same function. In repeated, exhaustive tests, both are shown to produce exactly the same quality of widget, at the same rate, with the same raw materials. Both produce the same amount of waste. Both consume the same amount of electrical power. They cost the same. In other words, their performance is identical in every measurable way. The only noticeable difference is that device #1 is much simpler than device #2. It contains fewer components and mechanisms, and its operating principle is therefore simpler. Which one would you choose?
Suppose the salesman for device #2 is quite upset that you are leaning toward device #1, and he promises to do better. The next day, he returns with a new device (we'll call it device #3) which is completely sealed in black plastic (the classic "black box"). He says it's the latest, most advanced widget-making machine in the world. You feed it electricity and raw materials, and it spits out widgets. Its performance is no different from device #1 and device #2, but it is not user servicable. You can't see inside to figure out how it works, and the salesman refuses to let you see diagrams or schematics, ostensibly because the operation of the machine is beyond both your intellectual capacity and his. The salesman argues that device #3 is actually simpler than both device #1 and #2 because it has just one component: the black box. Does this make sense to you? Again, which device would you choose?
Occam's Razor is merely a name given to a logical and intuitively obvious thought process of eliminating redundancies. It cannot be used to choose between competing theories whose predictions are vastly different, any more than the simplicity of a drill press can be used to prove that it's superior to a fighter plane. Now that we are equipped with an understanding of the reasoning behind Occam's Razor, we can list some of the reasons that it cannot be used to support either creationism or the existence of God:
-
Occam's Razor is a method of choosing between competing scientific theories. It is irrelevant when comparing a scientific theory to the concept of God or creationism because God and creationism are not scientific theories. There are no objective terms in the concept of God. No equations. No mechanisms. No limits. No methods through which it can be used to predict the outcome of natural processes. No methods through which it can be tested, or disproven. The concept of God is actually the antithesis of a scientific theory, in that one resorts to the divine only when one's reason has either failed or been voluntarily suppressed. In the analogy above, Occam's Razor was used to evaluate a pair of machines. It couldn't be used to evaluate a machine versus, say, a piece of music.
-
"God" is actually not a "simpler theory" than science. "God" is merely a three-letter name which is affixed to a deity whose machinations are supposedly so complex that they are beyond mortal comprehension! If God's methods are inscrutable and incomprehensible to humans (as claimed in the Bible and by all Christians), then what business does anyone have claiming that they are "simpler" than a theory which humans can understand? In the analogy above, the concept of God is very much like the "black box". The salesman may argue that it's simpler because it's a nice smooth black box instead of a set of gears and motors, but that's a childish superficiality at best, and a bald-faced lie at worst.
-
Occam's Razor is not invoked unless the competing theories make identical predictions. It is a method of eliminating redundancies, as William of Occam first reasoned, and it only applies when the performance of the competing theories is identical. When two theories make vastly different predictions (as is the case with science and Biblical literalism), then Occam's Razor is completely irrelevant. In the analogy above, Occam's Razor was used to evaluate a pair of machines whose performance was identical. If the two machines made widgets of vastly different characteristics, Occam's Razor would be irrelevant.
The use of Occam's Razor to "prove" the existence of God or the validity of Biblical literalism is a classic example of creationist pseudoscience, because it is so emblematic of their method: take a real principle and grossly misinterpret it to mean the exact opposite of what it truly means.
![]()
"The second law of thermodynamics makes evolution impossible. It states that complexity cannot be spontaneously created, so it is impossible for natural processes to create a complex organism from a simple organism!"
This is one of the oldest, and most popular creationist pseudoscience arguments. It's been kicking around for more than a century, thanks to general public ignorance of thermodynamics. In fact, it's wrong on so many levels that it's hard to know where to start! Perhaps we should start at the beginning, with the definition of the second law of thermodynamics. According to my engineering thermodynamics textbook, the second law of thermodynamics has two basic postulates:
-
All physical processes create entropy (microscopic disorder).
-
The entropy of a closed system cannot decrease, ie- entropy can be created but not destroyed.
That's a lot different from "complexity cannot be spontaneously created", isn't it? Big surprise- creationists don't know anything about thermodynamics. Now that we've established their bizarre misconception about the second law of thermodynamics, we should try to understand what strange mental contortions were necessary to go from "the entropy of a closed system cannot decrease" to "complexity cannot be spontaneously created."
Upon further questioning, creationists invariably reveal the following beliefs about the second law:
"The entropy of a living organism can't decrease."
"The creation of complexity requires the destruction of entropy."
"The second law of thermodynamics applies to spontaneous events, but not to the deliberate acts of man (or deity). That's why humans can build a complex structure but natural processes can't."
These three beliefs are all completely wrong, and they all indicate a frightening ignorance of scientific principles. Let us examine each belief separately:
-
Actually, the entropy of a living organism can decrease, because a living organism is not a closed system. Since it is an open system, entropy can leave and enter. Entropy doesn't have to be destroyed- just moved. The concept of the closed system vs the open system is one of the most basic concepts that we teach kids in high school, and if someone thinks a living organism is a closed system, he must be staggeringly ignorant. Food, water, and energy enter and leave your body all the time, thus making it an open system. Furthermore, an entire species is even less of a closed system than an individual life form, and evolution occurs from one generation to the next, not in a single organism as it ages.
-
Complexity is not the destruction of disorder or the creation of order. In fact, there is more disorder in complex systems, as any student of chaos theory (or government bureacracies) can tell you. There is far more entropy in a nuclear power plant than there is in an ice cube, and a pretty snowflake has much more complexity than the drop of water from whence it came.
-
Physical laws apply all the time, to everybody, regardless of intent or intelligence. If the second law of thermodynamics truly prohibited the creation of complexity, then it wouldn't matter whether the complexity is created by "deliberate" acts or by random happenstance- it would be impossible in both cases. It is utterly unbelievable to me that creationist ignoramuses would interpret any physical law to only apply in the absence of deliberate intervention. No other physical laws of physics are interpreted to apply only in the absence of intelligent intervention- does gravity shut off when humans intervene?
This argument has been so thoroughly disproven, so many times in so many ways, that it's almost comical when people keep bringing it up. They might as well just tattoo their foreheads with the words "scientific ignoramus."
![]()
"By taking a random mixture of elements and analysing the probability of elements randomly forming into the correct combinations and orientations to make a simple amino acid, I can show that it is probabilistically impossible for the simplest amino acid to form, never mind the first living cell. Therefore, a Creator must have formed the first organisms, if not all of them."
This argument is invalid for the following reasons:
-
Spontaneous formation of amino and fatty acids has been observed in the laboratory, by subjecting an atmosphere of hydrogen, water vapour, ammonia and methane to electrical discharges and ultraviolet radiation. This simulates primeval Earth environmental conditions, therefore it is an observed fact, and not subject to debate.
-
Chemical reactions are not random! Elements only bond in certain combinations. Light a match in a cloud of hydrogen and oxygen, and countless trillions upon trillions of hydrogen and oxygen atoms will react to form H2O. Not H8O, and not H5O, but H2O. Purely random combinatorics are a completely invalid way of modelling chemical reactions.
-
The first living cell did not have to form from raw materials. It would have formed from more primitive components such as RNA, which was proposed many years ago as the first self-replicating molecule. It was even experimentally found to have catalytic capabilities for adding new nucleotides to the end of the chain or removing them, leading to the term "RNA World" to describe the origins of life. But even if RNA is not the candidate we're looking for, there is certainly no need to assume that the first organic self-replicators would have been full-blown single-celled organisms. The early self-replicators (such as RNA, if it was indeed the first self-replicator) would not have left fossils.
-
This entire attack is a red herring, because evolution theory and abiogenesis (the formation of organic self-replicators from simpler organic materials) are two completely different theories. Lumping them together is just as fallacious as lumping evolution theory with Big Bang theory. The process of evolution is heritable change in populations over multiple generations. Because the process of evolution requires multiple generations to occur, it cannot possibly happen before the first living organism! It doesn't kick in until after the first living organism already exists! Even if abiogenesis could be disproved, evolution theory would still be valid.
I should also note that this argument is generally coupled with the fallacious reasoning that "anything we don't understand is proof of divine intervention." Poorly understood phenomena are not invalidations of science- they are opportunities for scientific investigation. If we treat every gap in our understanding as proof of divine intervention, we would be no better than the tribal primitives who attributed divine intervention to everything from solar eclipses to rain. Visit the Probability page if you want to know more.
![]()
"Some older species fossils can be found on top of newer fossils. This inconsistency in your so-called 'progressionism' proves that creation theory is correct, since it means that all species were created at the same time."
More bad science, since this only occurs with animal remains that are on the surface. What happens is that severe erosion or a geological upheaval can occasionally expose strata bearing fossils, and of course, when Skippy the Dog runs away and dies near these old fossils, the "Young Earth Creationist" crowd immediately interprets this as disproof of the entire fossil record, the entire field of geology, the age of the Earth, etc.
As usual, their argument is based on ignorance of proper scientific method. This evidence would be disproof of the fossil record if it was impossible to rationalize its existence with that record. However, that is simply not the case. Geologists can examine patterns in the rock to determine whether a region is old or new, cross-cut, the result of upheaval, etc. It is the creationists who will look at a region, assume its age without using proper methodology, and then use fossil findings in that region to "disprove" geology and evolution theory.
![]()
"Evolution can explain changes in a species, but where does a whole new species come from? Speciation is the downfall of Evolution Theory!"
This is another case of creationists projecting their own pseudoscientific attitudes onto evolution theory. In this case, they are predisposed to believe that the creation of a species is a sudden, dramatic event at some fixed moment in time. One moment there's species A, and then the next moment there's species B. Much as God created Man from dust, and Eve from Adam's rib, they imagine that "evolutionists" describe evolution creating a man directly from an ape. But evolution theory does not work that way.
Speciation is not a sudden, miraculous transformation from one species to another. The way creationists envision evolution theory, a pregnant female ape went into labour one day and a human being popped out! It is a gross understatement to say that this is a misrepresentation of the truth. In reality, evolution theory merely proposes that a great many small changes eventually caused an animal population to become intersterile with its ancestors.
Of course, this would mean that there should be fossil evidence of various intermediate stages between successful species, and there is. Naturally, creationists explain all of the evidence away by pointing the finger at their favourite whipping boy: the global conspiracy of evil scientists, who work tirelessly to cover up the truth and fabricate false evidence. These people watch "X-Files" too damned much.
![]()
"I know we've observed micro-evolution, but what about macro-evolution? There is no evidence for macro-evolution!"
The creationist invention of the terms "macroevolution" and "microevolution" is a good example of how they try to mutilate the terms of science to their own advantage. Biologists do not differentiate between micro-evolution and macro-evolution, any more than mathematicians differentiate between micro-addition and macro-addition.
Their argument that there is no evidence for "macroevolution" is ridiculous because "macroevolution" is simply the result of adding a lot of "microevolution" together, and "microevolution" is, by their own admission, completely supported by various forms of evidence.
The other problem for this argument is that there actually is evidence to directly support what they describe as "macroevolution", and it's called "the fossil record". It's evidence because it is consistent with prediction. Of course, that's not enough for the creationists- they demand direct observation of massive evolutionary change in living animals, even though they know that we would have to observe living animals for millions of years in order to obtain the evidence they seek. Can you see the problem with this demand? It's pretty obvious- they are deliberately asking for a form of evidence which is impossible to obtain (millions of years of direct observation), and ignoring a form of evidence (the fossil record) which is relatively easy to obtain.
The universe operates on tiny processes, affecting tiny particles, which add up in tremendous numbers to cause large changes. If someone is going to claim that a slow, steady process cannot create large-scale changes given sufficient time, he had better provide some evidence and reasoning, rather than simply stating it as a fact and demanding impossible forms of evidence to disprove it. Are we to assume that all gradual processes eventually hit "brick walls" and stop, for mysterious and unknown reasons?
Do we question tectonic plate theory on the basis that we've observed small-scale tectonic plate movement but not large-scale tectonic plate movement? Do we insist that no one should believe in tectonic plate theory until we've been able to observe it for millions of years, so we can see long-distance movements firsthand? Do we deny the possibility of large-scale rock erosion because we've only seen small scale rock erosion? Why would a gradual process like tectonic plate movement, rock erosion, or evolution suddenly stop after an arbitrary length of time? What would make it stop? Why make this ridiculous distinction between "micro-evolution" and "macro-evolution?" Where is the line drawn between the two? What causes the barrier? These are questions that the creationists don't attempt to ask or answer, because like O.J. Simpson's defense lawyers, they're not serious about uncovering the truth. They just want to create "reasonable doubt" in the minds of a gullible audience.
The "microevolution vs macroevolution" argument is an example of creationists projecting their own mentality onto evolution, and then attacking the resulting strawman, ironically, for the very aspects that come from creationism. Creationism describes separate and distinct species: "each according to its kind". Creationists therefore make the same assumption: species are separate, indivisible, and disconnected. When they project this mentality onto evolution, they run into an obvious problem: there is no way for the process of evolution to "jump" over the invisible "barrier" between species. The problem is that they are assuming that this barrier exists! The terms "microevolution" and "macroevolution" are not found in biology; they are creationist inventions. Gradual changes eventually add up, and can turn one species into two, or they can cause a species to change so much that it becomes a distinct species from its predecessors.
As a thought experiment, consider human beings. It is generally assumed that any male/female pair of healthy human beings can produce children. But biological reproduction is a complex process, and it requires great genetic commonality. We know that two modern human beings can produce children, but what about a modern woman and a man from ten thousand years ago? What about a modern woman and a man from fifty thousand years ago? Is there still enough genetic commonality? Species are not delineated by distinct, clear boundaries. Rather, they are defined by intersterility and overt physical characteristics, and there is no "barrier" between species for the process of evolution to hurdle.
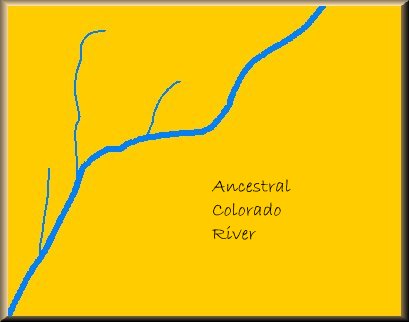 Prior to about 35 million years ago the ancestral Colorado River flowed across a vast plain, along a course very similar to that of today.
Prior to about 35 million years ago the ancestral Colorado River flowed across a vast plain, along a course very similar to that of today.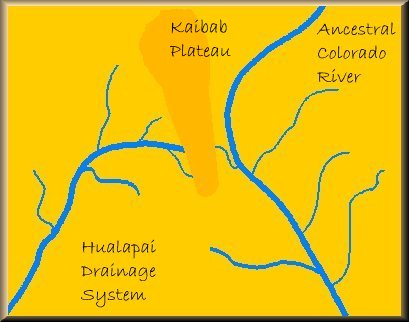 When the Kaibab Plateau began to uplift approximately 35 million years ago the river was diverted to the southeast because it could not cross newly created barrier. The new course for the river now flowed out to the Gulf of Mexico instead of to the Pacific Ocean. The old course on west side of the Kaibab Plateau, the Hualapai Drainage System, continued to be a major drainage for the plateau itself and the regions west of it.
When the Kaibab Plateau began to uplift approximately 35 million years ago the river was diverted to the southeast because it could not cross newly created barrier. The new course for the river now flowed out to the Gulf of Mexico instead of to the Pacific Ocean. The old course on west side of the Kaibab Plateau, the Hualapai Drainage System, continued to be a major drainage for the plateau itself and the regions west of it.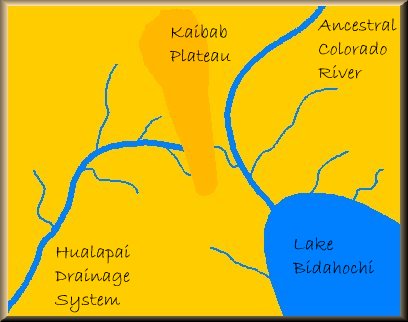 At some point around 12 million years ago, the river's course to the Gulf of Mexico became blocked and an enormous lake, know referred to as Lake Bidahochi, was formed as a result.
At some point around 12 million years ago, the river's course to the Gulf of Mexico became blocked and an enormous lake, know referred to as Lake Bidahochi, was formed as a result.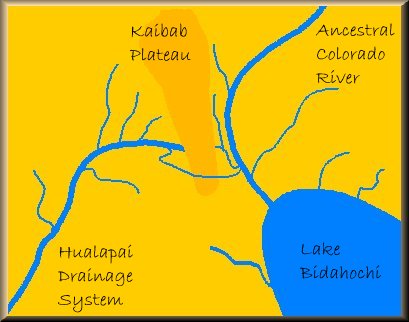 Meanwhile, on the western side of the Kaibab Plateau, a process known as "headwater erosion" began eating its way through the southern portion of the plateau. After millions of years this erosional process allowed the Hualapai system to break through the barrier created by the uplifted plateau and rejoin the ancestral Colorado.
Meanwhile, on the western side of the Kaibab Plateau, a process known as "headwater erosion" began eating its way through the southern portion of the plateau. After millions of years this erosional process allowed the Hualapai system to break through the barrier created by the uplifted plateau and rejoin the ancestral Colorado.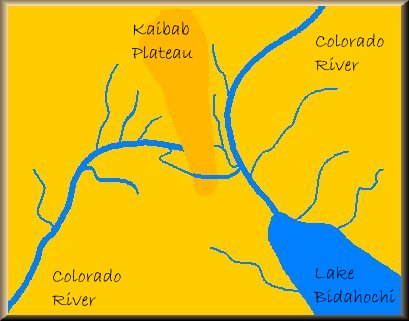 Once the break-through was complete the ancestral Colorado River began to follow the new course becuase of its steeper and more desirable descent. The waters of Lake Bidahochi began to drain through the new course as well and the result is the gorge through which the Little Colorado River now flows. The combined flow of the Colorado River and the Little Colorado River west of their confluence continued to widen and deepen the course and created the Grand Canyon.
Once the break-through was complete the ancestral Colorado River began to follow the new course becuase of its steeper and more desirable descent. The waters of Lake Bidahochi began to drain through the new course as well and the result is the gorge through which the Little Colorado River now flows. The combined flow of the Colorado River and the Little Colorado River west of their confluence continued to widen and deepen the course and created the Grand Canyon.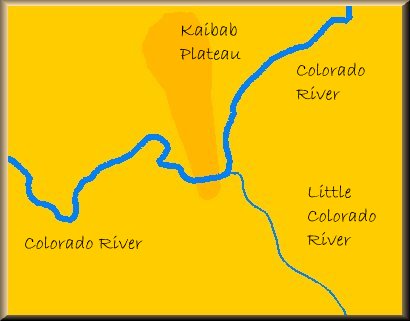 After Lake Bidahochi was drained the space that it once occupied was replaced by the Little Colorado River drainage system.
After Lake Bidahochi was drained the space that it once occupied was replaced by the Little Colorado River drainage system.