Posted on 02/08/2005 3:50:43 AM PST by PatrickHenry
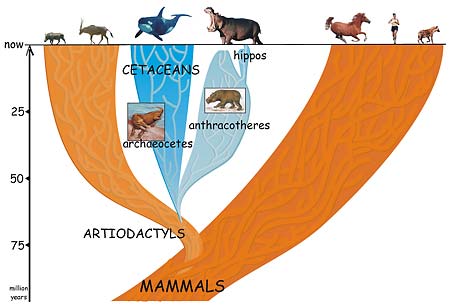
A group of four-footed mammals that flourished worldwide for 40 million years and then died out in the ice ages is the missing link between the whale and its not-so-obvious nearest relative, the hippopotamus.
The conclusion by University of California, Berkeley, post-doctoral fellow Jean-Renaud Boisserie and his French colleagues finally puts to rest the long-standing notion that the hippo is actually related to the pig or to its close relative, the South American peccary. In doing so, the finding reconciles the fossil record with the 20-year-old claim that molecular evidence points to the whale as the closest relative of the hippo.
"The problem with hippos is, if you look at the general shape of the animal it could be related to horses, as the ancient Greeks thought, or pigs, as modern scientists thought, while molecular phylogeny shows a close relationship with whales," said Boisserie. "But cetaceans – whales, porpoises and dolphins – don't look anything like hippos. There is a 40-million-year gap between fossils of early cetaceans and early hippos."
In a paper appearing this week in the Online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Boisserie and colleagues Michel Brunet and Fabrice Lihoreau fill in this gap by proposing that whales and hippos had a common water-loving ancestor 50 to 60 million years ago that evolved and split into two groups: the early cetaceans, which eventually spurned land altogether and became totally aquatic; and a large and diverse group of four-legged beasts called anthracotheres. The pig-like anthracotheres, which blossomed over a 40-million-year period into at least 37 distinct genera on all continents except Oceania and South America, died out less than 2 and a half million years ago, leaving only one descendent: the hippopotamus.
This proposal places whales squarely within the large group of cloven-hoofed mammals (even-toed ungulates) known collectively as the Artiodactyla – the group that includes cows, pigs, sheep, antelopes, camels, giraffes and most of the large land animals. Rather than separating whales from the rest of the mammals, the new study supports a 1997 proposal to place the legless whales and dolphins together with the cloven-hoofed mammals in a group named Cetartiodactyla.
"Our study shows that these groups are not as unrelated as thought by morphologists," Boisserie said, referring to scientists who classify organisms based on their physical characteristics or morphology. "Cetaceans are artiodactyls, but very derived artiodactyls."

The origin of hippos has been debated vociferously for nearly 200 years, ever since the animals were rediscovered by pioneering French paleontologist Georges Cuvier and others. Their conclusion that hippos are closely related to pigs and peccaries was based primarily on their interpretation of the ridges on the molars of these species, Boisserie said.
"In this particular case, you can't really rely on the dentition, however," Boisserie said. "Teeth are the best preserved and most numerous fossils, and analysis of teeth is very important in paleontology, but they are subject to lots of environmental processes and can quickly adapt to the outside world. So, most characteristics are not dependable indications of relationships between major groups of mammals. Teeth are not as reliable as people thought."
As scientists found more fossils of early hippos and anthracotheres, a competing hypothesis roiled the waters: that hippos are descendents of the anthracotheres.
All this was thrown into disarray in 1985 when UC Berkeley's Vincent Sarich, a pioneer of the field of molecular evolution and now a professor emeritus of anthropology, analyzed blood proteins and saw a close relationship between hippos and whales. A subsequent analysis of mitochondrial, nuclear and ribosomal DNA only solidified this relationship.
Though most biologists now agree that whales and hippos are first cousins, they continue to clash over how whales and hippos are related, and where they belong within the even-toed ungulates, the artiodactyls. A major roadblock to linking whales with hippos was the lack of any fossils that appeared intermediate between the two. In fact, it was a bit embarrassing for paleontologists because the claimed link between the two would mean that one of the major radiations of mammals – the one that led to cetaceans, which represent the most successful re-adaptation to life in water – had an origin deeply nested within the artiodactyls, and that morphologists had failed to recognize it.
This new analysis finally brings the fossil evidence into accord with the molecular data, showing that whales and hippos indeed are one another's closest relatives.
"This work provides another important step for the reconciliation between molecular- and morphology-based phylogenies, and indicates new tracks for research on emergence of cetaceans," Boisserie said.
Boisserie became a hippo specialist while digging with Brunet for early human ancestors in the African republic of Chad. Most hominid fossils earlier than about 2 million years ago are found in association with hippo fossils, implying that they lived in the same biotopes and that hippos later became a source of food for our distant ancestors. Hippos first developed in Africa 16 million years ago and exploded in number around 8 million years ago, Boisserie said.
Now a post-doctoral fellow in the Human Evolution Research Center run by integrative biology professor Tim White at UC Berkeley, Boisserie decided to attempt a resolution of the conflict between the molecular data and the fossil record. New whale fossils discovered in Pakistan in 2001, some of which have limb characteristics similar to artiodactyls, drew a more certain link between whales and artiodactyls. Boisserie and his colleagues conducted a phylogenetic analysis of new and previous hippo, whale and anthracothere fossils and were able to argue persuasively that anthracotheres are the missing link between hippos and cetaceans.
While the common ancestor of cetaceans and anthracotheres probably wasn't fully aquatic, it likely lived around water, he said. And while many anthracotheres appear to have been adapted to life in water, all of the youngest fossils of anthracotheres, hippos and cetaceans are aquatic or semi-aquatic.
"Our study is the most complete to date, including lots of different taxa and a lot of new characteristics," Boisserie said. "Our results are very robust and a good alternative to our findings is still to be formulated."
Brunet is associated with the Laboratoire de Géobiologie, Biochronologie et Paléontologie Humaine at the Université de Poitiers and with the Collège de France in Paris. Lihoreau is a post-doctoral fellow in the Département de Paléontologie of the Université de N'Djaména in Chad.
The work was supported in part by the Mission Paléoanthropologique Franco-Tchadienne, which is co-directed by Brunet and Patrick Vignaud of the Université de Poitiers, and in part by funds to Boisserie from the Fondation Fyssen, the French Ministère des Affaires Etrangères and the National Science Foundation's Revealing Hominid Origins Initiative, which is co-directed by Tim White and Clark Howell of UC Berkeley.
People view the universe as accidental for a reason--
All of us hate being found wrong in an argument. I know I do, and I have some scars from direct and indirect hits. I tend to post fast and loose.
The difference between myself and a creationist is that I am merely embarrassed when wrong. The creationist is afraid of eternal damnation for saying or believing the wrong thing. This is a hell of a way to go through life.
We got a glimpse of this attitude on the thread about Ernst Mayr -- FReeper who were certain of the state of his soul. The same smirking posts are made about Darwin, by FReeper who seem to know the activities of God in great personal detail.
The real debate here is not about who is right and who is wrong, but about how we form our opinions. Whether our motive is fear or curiosity.
The point is, with dogs we are observing speciation in action. Dogs at either end of the spectrum cannot inter-breed, whereas dogs that are closer together physically (say, a rottweiler and a standard poodle, imagine what that would look like) can. If we keep doing what we're doing with dogs, down the road the descendants of various breeds will certainly be considered different species.
Remember, we've only been messing with dogs for a few thousand years. Where do you think we'll be a million years from now?
Your second dishonest evasion of the question is noted.

I deal with the same problem in my field. Sigh.
You could just as easily assert that we are observing extinction in action-- you're assuming that some new thing is going to happen. I see a history of dwindling diversity in species, not expanding. Not that this makes me happy--but in a million years, I wonder if humans will be utterly alone with chickens, sheep and goats.
Very nice post BTW. Will be nice reading while I am in the lab tonight.
They had a gap in the record. Now they have two gaps. That's progress!
So go talk to someone else with your one-sentence magnificats...
I love this picture:
What I'm getting at here is that speciation isn't black and white. There are blurry dividing lines between species that haven't speciated quite far enough apart. So, a lion can inter-breed with a tiger, but not with a cheetah.
Does it actually say that He created plants and put them on earth, or does it say just that He created plants. Isn't it possible that plants existed on other planets before the earth existed?
Another "Ignorance is my strength" placemarker.
I was thinking more along the lines of Rosie ...
Here you go:

Not me, but the people who actually believe that a mammal went to the land, then went back to the water and develped some sort of mechanism to breath underwater or breach the water and breath air, they are the people who lost credibility.
If all you are going to do is point out my lack of desire to over type an answer, then you show you have no argument.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.