Schematic representation of possible mechanism of anaphylaxis reaction after mRNA vaccination for COVID-19:
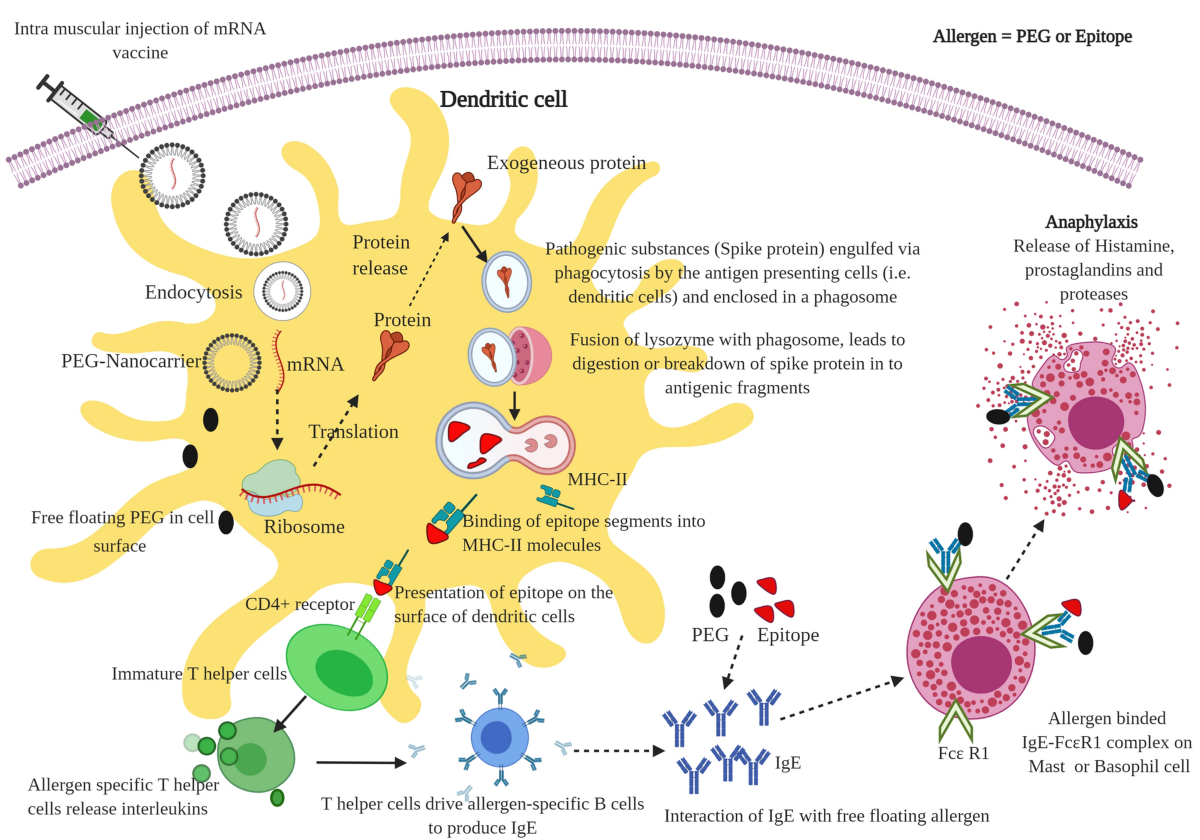
The mRNA free PEG in lipid nanoparticles floating on the cell surface interact with IgE antibodies (i.e. allergen) that bind into the FcƐR1 receptor on mast cells or basophils and can trigger immediate release of inflammatory and pro-inflammatory mediators that include histamine, prostaglandins, and proteases. Usually, the anaphylaxis signs and symptoms appear within a few minutes to one hour after exposure to allergic substances or antigens in the vaccine. Notably, allergens are mostly the proteins or glycoproteins or excipients present in the therapeutic molecules (e.g., vaccines) that promote or stimulate allergen-specific antibodies (i.e., immunoglobulins type E or IgE) in the human body [8]. These allergens react with IgE and cause allergic inflammatory responses. The crosslinking of IgE antibodies that are bound to the Fc epsilon RI (high-affinity IgE receptor) on the basophils and mast cells triggers degranulation in a short period. It results in the release of inflammatory mediators, namely histamine, prostaglandins and leukotrienes, proteases (G-protein-coupled receptors), and pro-inflammatory cytokines; and observation of major allergic symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, reddening, rashes, laryngeal edema, wheezing, tachycardia, hypotension, and cardiovascular collapse).