Posted on 04/30/2017 8:38:09 PM PDT by shove_it

A huge well of molten carbon that would spell disaster for the planet if released has been found under the US.
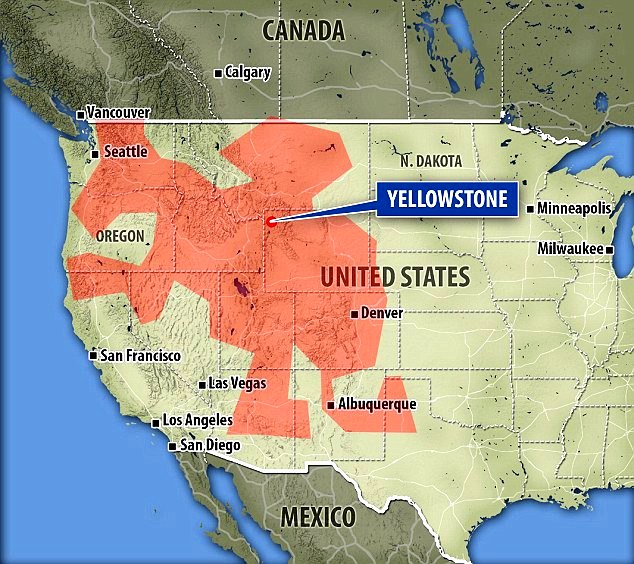
Scientists using the world's largest array of seismic sensors have mapped a deep-Earth area, covering 700,000 sq miles (1.8 million sq km).
This is around the size of Mexico, and researchers say it has the potential to cause untold environmental damage. The discovery could change our understanding of how much carbon the Earth contains, suggesting it is much more than we previously believed.
It would be impossible to drill far enough down to physically 'see' the Earth's mantle, so a team of researchers used a massive group of sensors to paint a picture of it, using mathematical equations to interpret their results.
The study, conducted by geologists at Royal Holloway University in London, used a huge network of 583 seismic sensors that measure the Earth's vibrations, to create a picture of the area's deep sub surface.
Known as the upper mantle, this section of the Earth's interior is known for by its high temperatures where solid carbonates melt, creating distinctive seismic patterns.
What they found was a vast buried deposit of molten carbon, which produces carbon dioxide and other gases, situated under the Western US, 217 miles (350km) beneath the Earth's surface. As a result of this study, published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters, scientists now believe the amount of CO2 in the Earth's upper mantle may be up to 100 trillion metric tons.
In comparison, the US Environmental Protection Agency estimates the global carbon emission in 2011 was nearly 10 billion metric tons – a tiny amount in comparison.
The deep carbon reservoir discovered will eventually make its way to the surface through volcanic eruptions and contribute to climate change albeit very slowly, but a sudden release could have dire consequences.
Dr Sash Hier-Majumder of the University of London's Department of Earth Sciences led the study. He said: 'The residence time of this carbon in the mantle is relatively large (nearly 1 billion years), so this reserve is not an imminent threat.'
'But one important mechanism by which carbon, sinking into the mantle via a subducting oceanic plate, can make it's way back to the surface is by arc volcanism.'
'Arc volcanism returns between 30-40% of the total subducted carbon back into the atmosphere. The remaining carbon stays in the mantle for a much longer.'
He added: 'We might not think of the deep structure of the Earth as linked to climate change above us, but this discovery not only has implications for subterranean mapping but also for our future atmosphere,'
'For example, releasing only one per cent of this CO2 into the atmosphere will be the equivalent of burning 2.3 trillion barrels of oil.'
'The existence of such deep reservoirs show how important is the role of deep Earth in the global carbon cycle.' As a result of this study, scientists now believe the amount of CO2 in the Earth's upper mantle may be up to 100 trillion metric tons.
In comparison, the US Environmental Protection Agency estimates the global carbon emission in 2011 was nearly 10 billion metric tons – a tiny amount in comparison. The area covered by the study includes Yellowstone National Park, where previous research has uncovered evidence of a supervolcano which could also spell danger for the planet.
The volcano at Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming and Montana sits atop a huge reserve of molten rock and last erupted 640,000 years ago.
It releases around 45,000 metric tonnes of carbon dioxide each day. If it were to erupt, it would be one thousand times as powerful as the 1980 Mount St Helens eruption and have the potential to blanket the US in a 'nuclear winter'.
While it has lain dormant for more than 70,000 years, scientists say that we can't rule out the possibility eruption this may some day take place - although they say the chances are extremely slim.
The Grand Prismatic hot spring in Yellowstone National Park is among the park's many hydrothermal features created by the Yellowstone supervolcano.
Experts say there is a one in 700,000 annual chance of a volcanic eruption at the site.
“Does this mean that SUVs can be found in the earths mantle?”
Maybe some Chevrolet Avalanches. What idiot at General Motors picked that name anyway?
Uhhh, they mean old discovery? We’ve known about that super volcano for years. How about we pop it and see if it solves the global warming hysteria?
Think of it as diamonds in the rough...
I was just reading somewhere that the “Ozone Hole” we were supposed to worry about opens up at the Poles during their respective winter months due to the fact that the Sun does not shine there. The Sun, which is supposed to burn us all alive through the Ozone Hole actually creates Ozone when it shines on the atmosphere, so that there will never be an “Ozone Hole” between us and the Sun. There will be an “Ozone Blanket” as needed, just as God intended.
Badly written article.
According to this https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/02/170213090756.htm it is “Under the western US is a huge underground partially-molten reservoir of liquid carbonate. It is a result of one of the tectonic plates of the Pacific Ocean forced underneath the western USA, undergoing partial melting thanks to gasses like CO2 and H2O contained in the minerals dissolved in it.”
Did they have to say “the size of Mexico”? Now the illegals will claim all that land too.
KT, sorry. Dyslexic typist.
The sky is falling! The sky is falling! Quick, send us more money, and we will prop it up!
OK, thanks. I was confused there. From the context, I should have known you meant the K-T boundary.<p
Molter carbon discovery is sure interesting, altogether.
Oh look — more carbon-causes-global-warming b******* from Europe.
We should drill down and tap that resource.
We could corner the global market on Bucky Balls and carbon nano tubes.
The molten carbon from down under would burst into flame upon exposure to the atmosphere, giving Algore a heart attack.
I’d agree, but note some of the other comments in the thread about what’s down there. Also, even the nitwit article author noted that we can’t drill down that far anyway, IOW, there’s not one little bit of danger of our opening a hole we can’t close, for example. :^)
Looks like a dancing GSD to me...
Worked for British Petroleum.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.