 The Four Chaplains, also sometimes referred to as the "Immortal Chaplains" or the "Dorchester Chaplains" were four United States Army chaplains who gave their lives to save other civilian and military personnel as the troop ship USAT Dorchester sank on February 3, 1943, during World War II. They helped other soldiers board lifeboats and gave up their own life jackets when the supply ran out. The chaplains joined arms, said prayers, and sang hymns as they went down with the ship. The Four Chaplains, also sometimes referred to as the "Immortal Chaplains" or the "Dorchester Chaplains" were four United States Army chaplains who gave their lives to save other civilian and military personnel as the troop ship USAT Dorchester sank on February 3, 1943, during World War II. They helped other soldiers board lifeboats and gave up their own life jackets when the supply ran out. The chaplains joined arms, said prayers, and sang hymns as they went down with the ship.
The Men The Four Chaplains, also sometimes referred to as the "Immortal Chaplains" or the "Dorchester Chaplains" were four United States Army chaplains who gave their lives to save other civilian and military personnel as the troop ship USAT Dorchester sank on February 3, 1943, during World War II. They helped other soldiers board lifeboats and gave up their own life jackets when the supply ran out. The chaplains joined arms, said prayers, and sang hymns as they went down with the ship. George L. Fox  George L. Fox was born March 15, 1900, in Lewistown, Pennsylvania, the eldest of eight children. When he was 17, he left school and lied about his age in order to join the Army to serve in World War I. He joined the ambulance corps in 1917, assigned to Camp Newton D. Baker in Texas. On December 3, 1917, George embarked from Camp Merritt, New Jersey, and boarded the USS Huron en route to France. As a medical corps assistant, he was highly decorated for bravery and was awarded the Silver Star, Purple Heart and the French Croix de Guerre. George L. Fox was born March 15, 1900, in Lewistown, Pennsylvania, the eldest of eight children. When he was 17, he left school and lied about his age in order to join the Army to serve in World War I. He joined the ambulance corps in 1917, assigned to Camp Newton D. Baker in Texas. On December 3, 1917, George embarked from Camp Merritt, New Jersey, and boarded the USS Huron en route to France. As a medical corps assistant, he was highly decorated for bravery and was awarded the Silver Star, Purple Heart and the French Croix de Guerre. Upon his discharge, he returned home to Altoona, where he completed high school. He entered Moody Bible Institute in Illinois in 1923. He and Isadora G. Hurlbut of Vermont were married in 1923, when he began his religious career as an itinerant preacher in the Methodist faith. He later graduated from Illinois Wesleyan University in Bloomington, served as a student pupil in Rye, New Hampshire, and then studied at the Boston University School of Theology, where he was ordained a Methodist minister on June 10, 1934. He served parishes in Union Village and Gilman, Vermont, and was appointed state chaplain and historian for the American Legion in Vermont. In 1942, Fox volunteered to serve as an Army chaplain, accepting his appointment July 24, 1942. He began active duty on August 8, 1942, the same day his son Wyatt enlisted in the Marine Corps. After Army Chaplains school at Harvard, he reported to the 411th Coast Artillery Battalion at Camp Davis. He was then united with Chaplains Goode, Poling and Washington at Camp Myles Standish in Taunton, Massachusetts, where they prepared to depart for Europe on board the USAT Dorchester. Alexander D. Goode  Reform-Rabbi Alexander D. Goode (Ph.D) was born in Brooklyn, New York on May 10, 1911, the son of Rabbi Hyman Goodekowitz. He was raised in Washington, D.C., attending Eastern High School, eventually deciding to follow his father's footsteps by studying for the rabbinate himself, at Hebrew Union College (HUC), where he graduated with a B.H. degree in 1937. He later received his Ph.D. from Johns Hopkins University in 1940. While studying for the rabbinate at HUC, he worked at the Washington Hebrew Congregation during summer breaks. Reform-Rabbi Alexander D. Goode (Ph.D) was born in Brooklyn, New York on May 10, 1911, the son of Rabbi Hyman Goodekowitz. He was raised in Washington, D.C., attending Eastern High School, eventually deciding to follow his father's footsteps by studying for the rabbinate himself, at Hebrew Union College (HUC), where he graduated with a B.H. degree in 1937. He later received his Ph.D. from Johns Hopkins University in 1940. While studying for the rabbinate at HUC, he worked at the Washington Hebrew Congregation during summer breaks. He originally applied to become a Navy chaplain in January 1941, but was not accepted. After the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, he applied to the Army, receiving his appointment as a chaplain on July 21, 1942. Chaplain Goode went on active duty on August 9, 1942, and was selected for the Chaplains School at Harvard. Chaplain Goode was then assigned to the 333rd Airbase Squadron in Goldsboro, North Carolina. In October 1942, he was transferred to Camp Myles Standish in Taunton, Massachusetts and reunited with Chaplains Fox, Poling and Washington, who were classmates at Harvard. Clark V. Poling  Clark V. Poling was born August 7, 1910, in Columbus, Ohio, the son of evangelical minister Dan Poling, who was rebaptized in 1936 as a Baptist minister. Clark Poling studied at Yale University's Divinity School in New Haven, Connecticut and graduated with his B.D. degree in 1936. He was ordained in the Reformed Church in America, and served first in the First Church of Christ, New London, Connecticut, and then as Pastor of the First Reformed Church, in Schenectady, New York. He married Betty Jung. Clark V. Poling was born August 7, 1910, in Columbus, Ohio, the son of evangelical minister Dan Poling, who was rebaptized in 1936 as a Baptist minister. Clark Poling studied at Yale University's Divinity School in New Haven, Connecticut and graduated with his B.D. degree in 1936. He was ordained in the Reformed Church in America, and served first in the First Church of Christ, New London, Connecticut, and then as Pastor of the First Reformed Church, in Schenectady, New York. He married Betty Jung. With the outbreak of World War II, Poling decided to enter the Army, wanting to face the same danger as others. His father, who had served as a World War I chaplain, told him chaplains risk and give their lives, too—and with that knowledge, he applied to serve as an Army chaplain, accepting an appointment on June 10, 1942 as a chaplain with the 131st Quartermaster Truck Regiment, reporting to Camp Shelby, Hattiesburg, Mississippi, on June 25. Later he reported to Army Chaplains School at Harvard, where he would meet Chaplains Fox, Goode, and Washington. John P. Washington  John P. Washington was born in Newark, New Jersey on July 18, 1908. He studied at Seton Hall, in South Orange, New Jersey, to complete his high school and college courses in preparation for the Catholic priesthood. He graduated in 1931 with an A.B. Degree, entering Immaculate Conception Seminary in Darlington, New Jersey, where he received his minor orders on May 26, 1933. He served as a subdeacon at all the solemn masses and later became a deacon on December 25, 1934. He was elected prefect of his class and was ordained a priest on June 15, 1935. John P. Washington was born in Newark, New Jersey on July 18, 1908. He studied at Seton Hall, in South Orange, New Jersey, to complete his high school and college courses in preparation for the Catholic priesthood. He graduated in 1931 with an A.B. Degree, entering Immaculate Conception Seminary in Darlington, New Jersey, where he received his minor orders on May 26, 1933. He served as a subdeacon at all the solemn masses and later became a deacon on December 25, 1934. He was elected prefect of his class and was ordained a priest on June 15, 1935. Father Washington's first parish was at St. Genevieve's, in Elizabeth, NJ. He later served at St. Venantius for a year. In 1938, he was assigned to St. Stephen's in Kearny, New Jersey. Shortly after the Pearl Harbor attack of December 7, 1941, he received his appointment as a chaplain in the United States Army, reporting for active duty on May 9, 1942. He was named Chief of the Chaplains Reserve Pool, in Ft. Benjamin Harrison, Indiana, and in June 1942, he was assigned to the 76th Infantry Division in Ft. George Meade, Maryland. In November 1942, he reported to Camp Myles Standish in Taunton, Massachusetts and met Chaplains Fox, Goode and Poling at Chaplains School at Harvard.
The Ship  The Dorchester was a 5,649 ton civilian cruise ship, 368 feet long with a 52-foot beam and a single funnel, originally built in 1926 by Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company, for the Merchants and Miners Line, operating ships from Baltimore to Florida, carrying both freight and passengers. It was the third of four liners being built for the Line. The Dorchester was a 5,649 ton civilian cruise ship, 368 feet long with a 52-foot beam and a single funnel, originally built in 1926 by Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company, for the Merchants and Miners Line, operating ships from Baltimore to Florida, carrying both freight and passengers. It was the third of four liners being built for the Line. The ship was converted for military service in World War II as a troop transport, and renamed United States Army Transport (USAT) Dorchester. The conversion was done in New York by the Atlantic, Gulf, and West Indies (AGWI) SS Company, and included additional lifeboats and liferafts; guns (a 3 inch 50 caliber gun forward, and a 4 inch 50 caliber gun aft, in addition to four 20mm guns); and changes to the large windows in the pilot house so that they would be reduced to slits to afford more protection. A liner designed for 314 passengers and 90 crew would now be able to carry slightly more than 900 passengers and crew.
The Story Dorchester left New York on January 23, 1943, en route to Greenland, carrying the four chaplains and approximately 900 others, as part of a convoy of three ships (SG-19 convoy). Most of the military personnel were not told the ship's ultimate destination. The convoy was escorted by Coast Guard Cutters Tampa, Escanaba, and Comanche. The ship's captain, Hans J. Danielsen, had been alerted that Coast Guard sonar had detected a submarine. Because German U-boats were monitoring sea lanes and had attacked and sunk ships earlier during the war, Captain Danielsen had the ship's crew on a state of high alert even before he received that information, ordering the men to sleep in their clothing and keep their life jackets on. "Many soldiers sleeping deep in the  ship's hold disregarded the order because of the engine's heat. Others ignored it because the life jackets were uncomfortable." ship's hold disregarded the order because of the engine's heat. Others ignored it because the life jackets were uncomfortable." During the early morning hours of February 3, 1943, at 12:55 a.m., the vessel was torpedoed by the German submarine U-223 off Newfoundland in the North Atlantic. The torpedo knocked out the Dorchester 's electrical system, leaving the ship dark. Panic set in among the men on board, many of them trapped below decks. The chaplains sought to calm the men and organize an orderly evacuation of the ship, and helped guide wounded men to safety. As life jackets were passed out to the men, the supply ran out before each man had one. The chaplains removed their own life jackets and gave them to others. They helped as many men as they could into lifeboats, and then linked arms and, saying prayers and singing hymns, went down with the ship.
As I swam away from the ship, I looked back. The flares had lighted everything. The bow came up high and she slid under. The last thing I saw, the Four Chaplains were up there praying for the safety of the men. They had done everything they could. I did not see them again. They themselves did not have a chance without their life jackets. —Grady Clark, survivor
According to some reports, survivors could hear different languages mixed in the prayers of the chaplains, including Jewish prayers in Hebrew and Catholic prayers in Latin. Some 230 of the 904 men aboard the ship were rescued. Life jackets offered little protection from hypothermia, which killed most men in the water. The water temperature was 34 °F (1 °C) and the air temperature was 36 °F (2 °C). By the time additional rescue ships arrived, "hundreds of dead bodies were seen floating on the water, kept up by their life jackets.
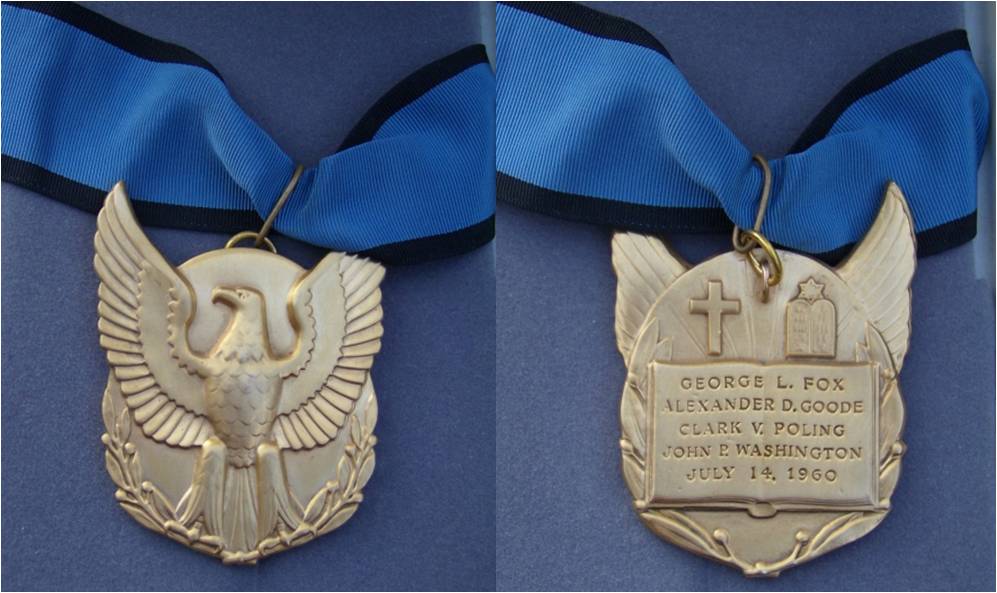
Awards On December 19, 1944, all four chaplains were posthumously awarded the Purple Heart and the Distinguished Service Cross. Main article: Four Chaplains' Medal Congress also attempted to confer the Medal of Honor on each of the four chaplains, but the stringent requirements for that medal required heroism performed “under fire,” and the bravery and ultimate sacrifice of these men did not technically qualify, since their actions took place after the torpedo attack. Therefore, members of Congress decided to authorize a special medal intended to have the same weight and importance as the Medal of Honor. This award, the Four Chaplains' Medal, was approved by a unanimous act of Congress on July 14, 1960, through Public law 86-656 of the 86th Congress. The medals were presented posthumously to the next of kin of each of the Four Chaplains by Secretary of the Army Wilber M. Brucker at Ft. Myer, Virginia on January 18, 1961. In 2006, National Executive Committee of The American Legion, at the Legion’s 88th National Convention in Salt Lake City, passed a resolution urging Congress to revisit the issue of awards, and award the Medal of Honor to Fox, Goode, Poling and Washington.
Remembrance Four Chaplains Day In 1988, February 3 was established by a unanimous act of Congress as an annual "Four Chaplains Day."Some state or city officials commemorate the day with official proclamations, sometimes including the order that flags fly at half-mast in memory of the fallen chaplains. In some cases, official proclamations establish observances at other times: for example, North Dakota legislation requests that the Governor issue an annual proclamation establishing the first Sunday in February as "Four Chaplains Sunday." The day is also observed as a feast day on the liturgical calendar of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America US Postage Stamp The chaplains were honored with a commemorative stamp that was issued in 1948, and was designed by Louis Schwimmer, the head of the Art Department of the New York branch of the U.S. Post Office Department (now called the USPS). This stamp is highly unusual, because until 2011, U.S. stamps were not normally issued in honor of someone other than a President of the United States until at least ten years after his or her death. death. The stamp went through three revisions before the final design was chosen. None of the names of the chaplains were included on the stamp, nor were their faiths (although the faiths had been listed on one of the earlier designs): instead, the words on the stamp were "These Immortal Chaplains...Interfaith in Action." Another phrase included in an earlier design that was not part of the final stamp was "died to save men of all faiths." By the omission of their names, the stamp commemorated the event, rather than the individuals per se, thus obfuscating the ten-year rule in the same way as later did stamps honoring Neil Armstrong in 1969 and Buzz Aldrin in 1994. Chapel of Four Chaplains The Chapel of the Four Chaplains was dedicated on February 3, 1951, by President Harry S. Truman to honor these chaplains of different faiths in the basement of Grace Baptist church in Philadelphia. In 1974, that congregation moved to Blue Bell, and sold the building to Temple University. Today Temple University is renovating that building. In his dedication speech, the President said, “This interfaith shrine... will stand through long generations to teach Americans that as men can die heroically as brothers so should they live together in mutual faith and goodwill.” The Chapel dedication included a reminder that the interfaith team represented by the Four Chaplains was unusual. Although the Chapel was dedicated as an All-Faiths Chapel, no Catholic priest took part in the dedication ceremony, because, as Msgr. Thomas McCarthy of the National Catholic Welfare Conference explained to Time magazine, "canon law forbids joint worship." In addition to supporting work that exemplifies the idea of Interfaith in Action, recalling the story of the Four Chaplains, the Chapel presents awards to individuals whose work reflects interfaith goals. 1984 was the first time that the award went to a military chaplain team composed of a rabbi, priest, and minister, recalling in a special way the four chaplains themselves, when the Rabbi Louis Parris Hall of Heroes Gold Medallion was presented to Rabbi Arnold Resnicoff; Catholic Priest Fr. George Pucciarelli; and Protestant Minister Danny Wheeler—the three chaplains present at the scene of the 1983 Beirut barracks bombing. The story of these three United States Navy Chaplains was itself memorialized in a Presidential speech by President Ronald Reagan, on April 12, 1984. Memorial Foundations The Four Chaplains Memorial Foundation, the only 501(c)(3) charity related to the Four Chaplains' legacy, is housed at the former U.S. Naval Chapel located at the former South Philadelphia Navy Yard. Its official mission statement is "to further the cause of 'unity without uniformity' by encouraging goodwill and cooperation among all people. The organization achieves its mission by advocating for and honoring people whose deeds symbolize the legacy of the Four Chaplains aboard the U.S.A.T. Dorchester in 1943." In addition to its other goals and objectives, it supports memorial services that honor the memory of the chaplains and tell their story by publishing Guidelines for Four Chaplains Interfaith Memorial Services. Additionally, it sponsors an "Emergency Chaplains Corps" to provide support for first responders in disaster situations, and scholarship competitions for graduating high school seniors, focusing on the values of "inclusion, cooperation, and unity" exemplified by the Four Chaplains story. The competitions include a National Art Scholarship contest, a National Essay Scholarship contest, and a National Project Lifesaver Scholarship contest. in 1943." In addition to its other goals and objectives, it supports memorial services that honor the memory of the chaplains and tell their story by publishing Guidelines for Four Chaplains Interfaith Memorial Services. Additionally, it sponsors an "Emergency Chaplains Corps" to provide support for first responders in disaster situations, and scholarship competitions for graduating high school seniors, focusing on the values of "inclusion, cooperation, and unity" exemplified by the Four Chaplains story. The competitions include a National Art Scholarship contest, a National Essay Scholarship contest, and a National Project Lifesaver Scholarship contest. The Immortal Chaplains Foundation was incorporated in October 1997 as a Minnesota non-profit corporation. The original concept for the Foundation was from David Fox, nephew of Chaplain George Fox, and Rosalie Goode Fried, the daughter of Chaplain Alexander Goode. The organization's goal is "to honor individuals, both past and present, whose lives exemplify the compassion of the four 'Immortal Chaplains' and who have risked all to protect others of different faith or ethnicity." The group presents an annual "Prize for Humanity," "to broaden national and international awareness of the legacy of the four 'Immortal Chaplains,'" "to inspire youth to the values of the four 'Immortal Chaplains,'" and "to find new partners and ways to tell this story and preserve the legacy." At the 1999 Award Ceremony, held in Minnesota, South African Bishop Desmond Tutu helped present Prizes for Humanity that included posthumous awards for Amy Biehl, an American Stanford University student and Fulbright scholar who was stabbed to death in South Africa while working to establish a Legal Education Center; and Charles W. David, an African-American Coast Guardsman on board the Coast Guard Cutter Comanche, who rescued many of the Dorchester survivors, later dying from pneumonia as a result of his efforts. Unfortunately, the establishment of the Immortal Chaplains Foundation included some controversy, when The Chapel of Four Chaplains sued Fox to prevent him and his new group from using the phrase "The Four Chaplains" or the image of them that appeared on the U.S. postage stamp. See more memorials at the source. |



![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()










![]()





