The referenced article requires a subscription to Science: http://science.sciencemag.org/content/352/6285/550 ABSTRACT: Wakefulness is driven by the widespread release of neuromodulators by the ascending arousal system. Yet, it is unclear how these substances orchestrate state-dependent, global changes in neuronal activity. Here, we show that neuromodulators induce increases in the extracellular K+ concentration ([K+]e) in cortical slices electrically silenced by tetrodotoxin. In vivo, arousal was linked to AMPA receptor–independent elevations of [K+]e concomitant with decreases in [Ca2+]e, [Mg2+]e, [H+]e, and the extracellular volume. Opposite, natural sleep and anesthesia reduced [K+]e while increasing [Ca2+]e, [Mg2+]e, and [H+]e as well as the extracellular volume. Local cortical activity of sleeping mice could be readily converted to the stereotypical electroencephalography pattern of wakefulness by simply imposing a change in the extracellular ion composition. Thus, extracellular ions control the state-dependent patterns of neural activity.
To: molewhacka
AMPA receptor–independent elevations of [K+]e concomitant with decreases in [Ca2+]e, [Mg2+]e, [H+]e, and the extracellular volume.
I was just saying that the other day.
To: molewhacka
Salts in our brain decide whether we are asleep or awake.
For the first time, researchers have shown that the level of salts in our body and brain differ depending on whether we are asleep or awake.
Correlation is not causation.
3 posted on
04/30/2016 5:44:46 AM PDT by
mountn man
(The Pleasure You Get From Life, Is Equal To The Attitude You Put Into It)
To: molewhacka
Opposite, natural sleep and anesthesia reduced [K+]e while increasing [Ca2+]e, [Mg2+]e, and [H+]e as well as the extracellular volume.Does this mean in laymen's terms that if you take a Calcium/Magnesium supplement that could somehow ensure that the elements would be better absorbed in the brain, you would be more likely to sleep well?
4 posted on
04/30/2016 5:46:27 AM PDT by
chajin
("There is no other name under heaven given among people by which we must be saved." Acts 4:12)
To: molewhacka
So does salt make you sleep or keep you awake?
To: molewhacka
Woohoo..!
This means I can have a giant, hot, soft pretzel before bedtime every night..!
6 posted on
04/30/2016 5:47:35 AM PDT by
Stormy_2021
(... Pear Pimples for Hairy Fishnuts..!)
To: molewhacka
I know it sounds odd, because it is a breakfast food.
But two or three sunny side eggs always knock me out pretty good!
Might be the tryptophan...
14 posted on
04/30/2016 5:54:46 AM PDT by
djf
("She wore a raspberry beret, the kind you find in a second hand store..." - Prince)
To: molewhacka
Here is the quick and dirty simple explanation of how neural transmission happens. This explaines the effect of both salts and calcium.
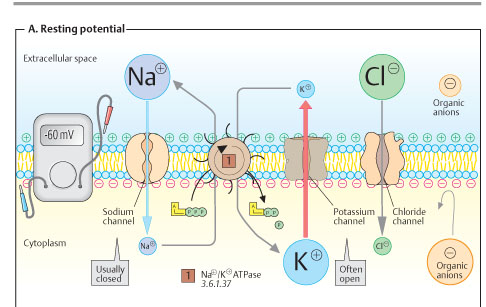
Neurons send messages electrochemically. This means that chemicals cause an electrical signal. Chemicals in the body are "electrically-charged" -- when they have an electrical charge, they are called ions. The important ions in the nervous system are sodium and potassium (both have 1 positive charge, +), calcium (has 2 positive charges, ++) and chloride (has a negative charge, -).
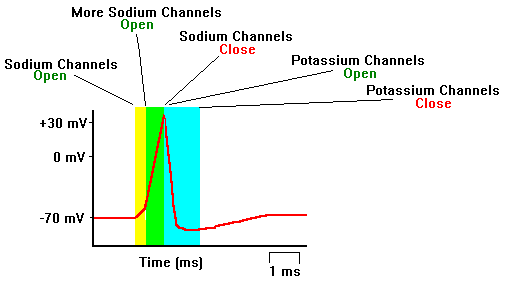
ACTION POTENTIAL: Reversal of RMP for a very short period on applying a stimulus. Value: + 30 to + 60 mV. It consists of 4 stages, namely:
a) Depolarization: Usually RMP = - 85 mV. When an impulse comes, polarization gets reversed, i.e., inside (+ve) and outside (-ve). This is known as depolarization. It rises sharply when RMP attains – 70 mV. It is also known as spike potential.
b) Repolarization: The restoration of normal RMP within a short time (1/2 of a msec). It starts fast but becomes slower and takes a longer period to reach the normal state. c) Negative after potential: Also known as After depolarization (AD). The slower and longer period taken to reach normal RMP (2 – 15 msec).
d) Positive after potential: Also known as After hyperpolarization (AH). Even after AD, the membrane potential becomes even more – ve than the normal (- 85 mV) and remains –ve for about 50 msec or longer.
To: molewhacka
Milk and milk products contain the sleep-inducing amino acid tryptophan.
Tryptophan is an amino acid that promotes sleep and is found in small amounts in all protein foods. It is a precursor to the sleep-inducing compounds serotonin (a neurotransmitter), and melatonin (a hormone which also acts as a neurotransmitter).
Thus, for tryptophan to have a sedative effect, it needs to enter the brain by crossing the blood-brain barrier. Additionally, since tryptophan uses the same transport system as other amino acids, it has to compete against them to enter the brain.
To: molewhacka
38 posted on
04/30/2016 6:33:47 AM PDT by
JoeProBono
(SOME IMAGES MAY BE DISTURBING ’VIEWER DISCRETION IS ADVISED;-{)
To: molewhacka
I have to say, it is really amusing to read non-scientists’ interpretations of this article!
The first section of Science magazine usually has a synopsis of its articles written in plain language for lay people to understand. And yes, the plain language synopsis is useful for us scientists who cannot possibly know the intricate details of scientific endeavors outside of our own fields of expertise. Perhaps the plain-language synopsis of this article would be more helpful to the non-scientist FReepers?
42 posted on
04/30/2016 6:50:52 AM PDT by
exDemMom
(Current visual of the hole the US continues to dig itself into: http://www.usdebtclock.org/)
To: molewhacka
Because salt makes you need to pee so you wake up?
50 posted on
04/30/2016 7:32:59 AM PDT by
SeeSharp
To: molewhacka
yeah, the “eureka” article is worthless, referring repeatedly to just “salts”.
Here’s a better article (that’s free):
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/ions-may-be-charge-when-you-sleep-and-wake
“Changes in ion concentrations, not nerve cell activity, switch the brain from asleep to awake and back again, researchers report in the April 29 Science. Scientists knew that levels of potassium, calcium and magnesium ions bathing brain cells changed during sleep and wakefulness. But they thought neurons — electrically active cells responsible for most of the brain’s processing power — drove those changes.
Instead, the study suggests, neurons aren’t the only sandmen or roosters in the brain. “Neuromodulator” brain chemicals, which pace neuron activity, can bypass neurons altogether to directly wake the brain or lull it to sleep by changing ion concentrations.
Scientists hadn’t found this direct connection between ions and sleep and wake before because they were mostly focused on what neurons were doing, says neuroscientist Maiken Nedergaard, who led the study. She got interested in sleep after her lab at the University of Rochester in New York found a drainage system that washes the brain during sleep (SN: 11/16/13, p. 7).When measuring changes in the fluid between brain cells, Nedergaard and colleagues realized that ion changes followed predictable patterns: Potassium ion levels are high when mice (and presumably people) are awake, and drop during sleep. Calcium and magnesium ions follow the opposite pattern; they are higher during sleep and lower when mice are awake.”
SO -— low potassium and high magnesium and high calcium could promote sleep. Guess that’s why so many say take a good magnesium supplement to promote sleep. I do this along with Vitamin D before bedtime. But take a GOOD mag supplest, namely a fully-reacted chelated one, NOT an inorganic one like mag oxide or mag citrate: those will only give you diarrhea.
56 posted on
04/30/2016 8:10:39 AM PDT by
catnipman
(Cat Nipman: Vote Republican in 2012 and only be called racist one more time!)
To: molewhacka
I wonder if certain individuals in comas would not respond to a salt treatment by waking up.
64 posted on
04/30/2016 8:44:09 AM PDT by
pierrem15
("Massacrez-les, car le seigneur connait les siens")
To: molewhacka

It's got what sleepyheads crave.
71 posted on
04/30/2016 9:30:18 AM PDT by
tumblindice
(America's founding fathers: all armed conservatives.)
To: molewhacka
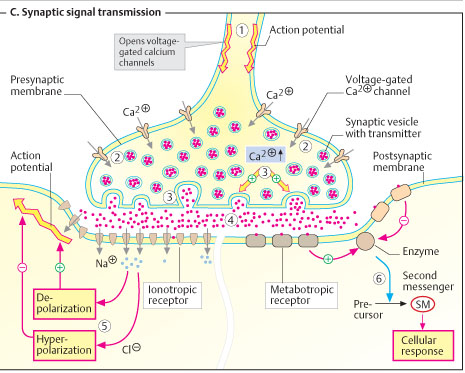
Helps set electrical bias which controls synaptic firing....
FreeRepublic.com is powered by software copyright 2000-2008 John Robinson




